Extended Data Fig 1. Overall workflow of intraoperative SRH and DeepGlioma.
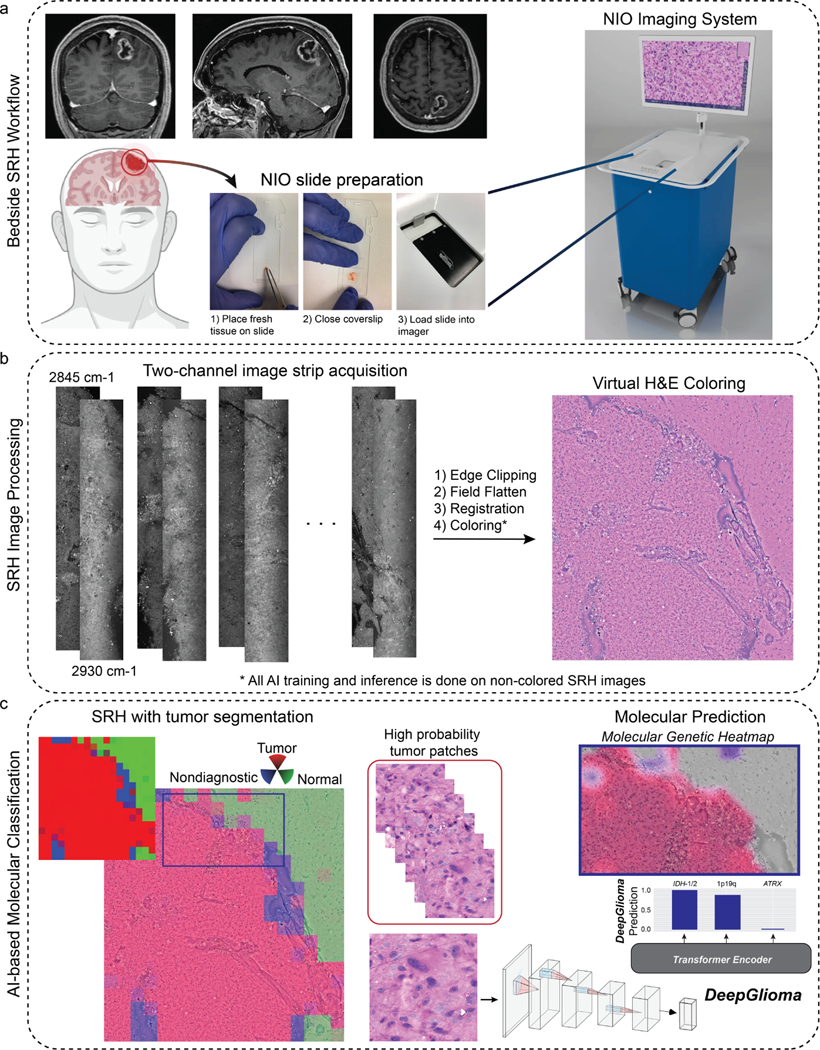
a, DeepGlioma for molecular prediction is intended for adult (≥ 18 years) patients with clinical and radiographic evidence of a diffuse glioma who are undergoing surgery for tissue diagnosis and/or tumor resection. The surgical specimen is sampled from the patient’s tumor and directly loaded into a premade, disposable microscope slide with attached coverslip. The specimen is loaded into the NIO Imaging System (Invenio Imaging, Inc., Santa Clara, CA) for rapid optical imaging. b, SRH images are acquired sequentially as strips at two Raman shifts, 2845 cm−1 and 2930 cm−1. The size and number of strips to be acquired is set by the operator who defines the desired image size. Standard images sizes range from 1–5mm2 and image acquisition time ranges from 30 seconds to 3 minutes. The strips are edge clipped, field flattened, and registered to generate whole slide SRH images. These whole slide images are then used for both DeepGlioma training and inference. Additionally, whole slide images can be colored using a custom virtual H&E colorscheme for review by the surgeon or pathologist [6]. c, For AI-based molecular diagnosis, the whole slide image is split into non-overlapping 300×300 pixel patches and each patch undergoes a feedforward pass through a previously trained network to segment the patches into tumor regions, normal brain, and nondiagnostic regions [19]. The tumor patches are then used by DeepGlioma at both training and inference to predict the molecular status of the patient’s tumor.
