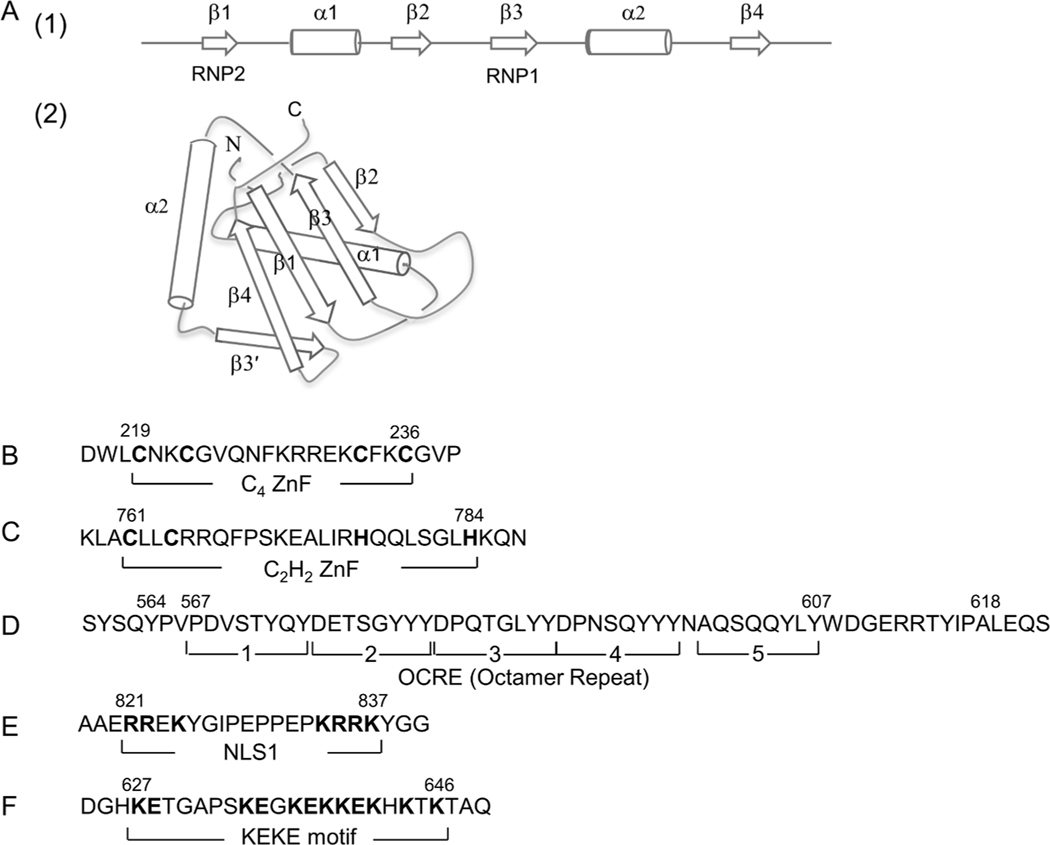
Fig. 2.
Domain structures of RBM10. (A) RNA recognition motifs (RRMs). (1) Schematic representation of a canonical RRM. RRM is composed of four β-sheets and two α-helices arranged in the order β1–α1–β2–β3–α2–β4. (2) 3D structure of RRM1. The figure schematically shows the RRM1 structure of RBM10 determined by NMR (Serrano et al., 2018; Protein Data Bank: 2LX1). The β3- and β1-strands containing RNP1 and RNP2 shown in panel (1) form an RNA-binding surface. (B and C) C4 ZnF and C2H2 ZnF. The cysteine and histidine residues critical for the C4- and C2H2-type ZnF structures and functions are highlighted in boldface. (D) OCRE (Octamer repeat). Brackets 1–5 represent five repeating octamers (8 aa) originally assigned based on hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity profiles (Inoue et al., 1996). The extended aa 564–618 forms a globular fold of 6 anti-parallel β-sheets (Martin et al., 2016). (E) NLS1. Basic aa residues in the bipartite sequence are highlighted. (F) KEKE region. Positive and negative aa residues characterizing the KEKE region are highlighted.