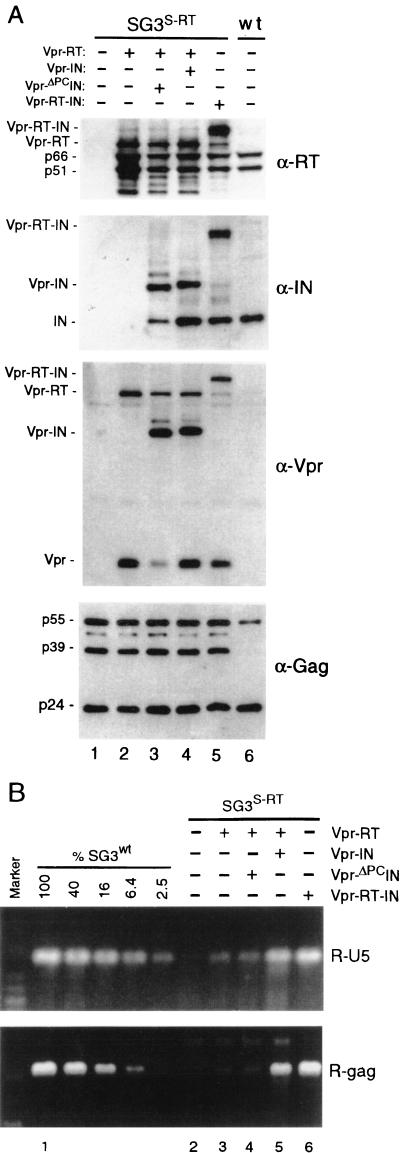
FIG. 3.
The trans-IN protein functions after virus assembly and proteolytic processing. Four micrograms of pSG3S-RT DNA was transfected into 293T cells (−) or cotransfected (+) with the Vpr-RT, Vpr-ΔPCIN, and Vpr-RT-IN expression vectors, respectively. (A) Immunoblot analysis. Transfection-derived virions were concentrated from the culture supernatants by ultracentrifugation (125,000 × g for 2 h) through cushions of 20% sucrose. The pellets were lysed and examined by immunoblot analysis with anti-RT (α-RT), anti-IN, anti-Vpr, and anti-Gag antibodies as indicated. (B) The trans-IN protein is required for viral DNA synthesis. Five hundred nanograms of the transfection-derived viruses was used to infect cultures of HeLa-CD4 cells. DNA products of reverse transcription were prepared and analyzed exactly as described above. The data are from a representative experiment that was repeated three times.