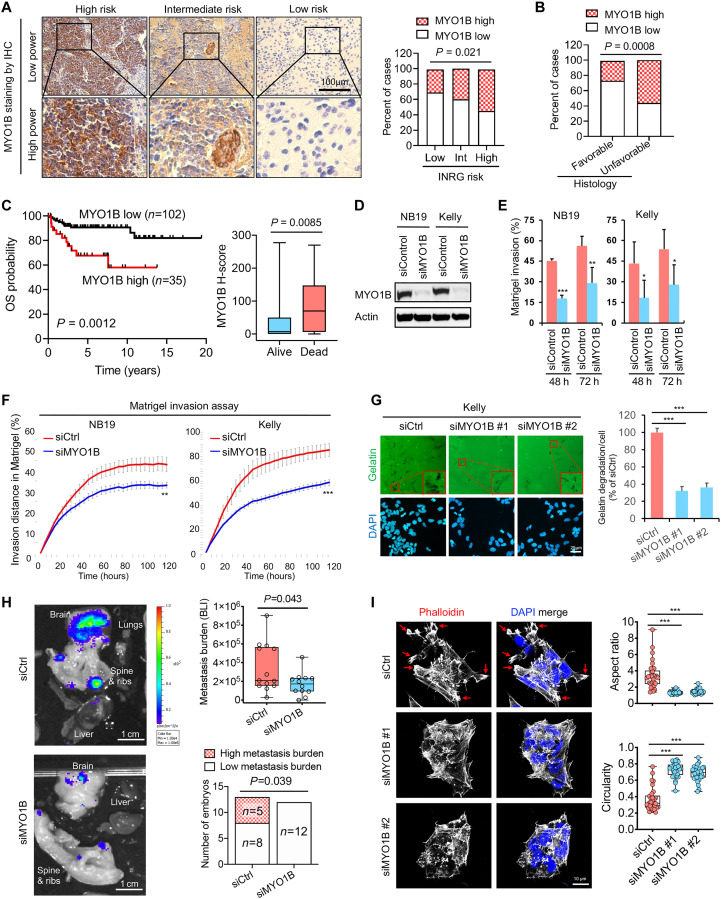
Fig. 4. MYO1B correlates with poor prognosis and promotes the invasive and metastatic capacity of MNA+ NB.
(A) Representative images (left panel) and statistics (right panel) showing MYO1B expression evaluated by IHC in NB with different INRG risks. (B) Statistics showing MYO1B expression assessed by IHC in NB with favorable versus unfavorable histology. (C) Prognostic significance of MYO1B protein expression (by IHC staining) in a cohort of 137 NB patients. (D to F) Impact of MYO1B depletion (D) on cell invasion through Matrigel was evaluated using ibidi four-well culture inserts (E) and Essen BioScience Incucyte 96-well scratch wound invasion assay (F) (n = 5 to 8). (G) Impact of MYO1B depletion on gelatin degradation capacity (n = 5). (H) Left panel: The impact of MYO1B depletion on the metastatic capacity of NB cells (luciferase-expressing Kelly cells) was evaluated using the chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) metastasis model. Right upper panel: Metastasis burden was measured by bioluminescent intensity (BLI) in each embryo; right lower panel: BLI over 5 × 105 was regarded as high metastasis burden. (I) The impact of MYO1B depletion on NB cell (Kelly) morphology was determined by actin cytoskeleton staining using phalloidin, and the aspect ratio and circularity were assessed using ImageJ software. Differences between groups were determined by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Fisher’s exact test was used to determine the associations between two categorical variables in two groups. Log-rank test was used in Kaplan-Meier survival analysis.