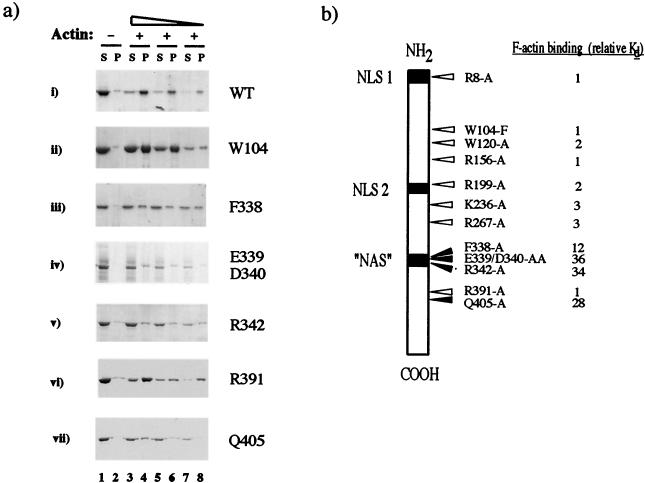
FIG. 5.
Identification of NP point mutations which disrupt actin binding. (a) WT or mutant MBP-NP polypeptides were cosedimented in the absence (−) or presence (+) of 3 μM F-actin, and supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions were examined by SDS-PAGE. (b) Summary of point mutations and cellular localization signals in NP. Arrows indicate the positions of amino acid changes introduced into NP. White arrows indicate mutations with no major effect on F-actin binding and black arrows indicate those that substantially reduced binding. Tabulated values are the fold decrease in binding affinity for F-actin relative to values for the WT protein. Also shown are the positions of the three postulated cellular localization signals that have been identified in NP.