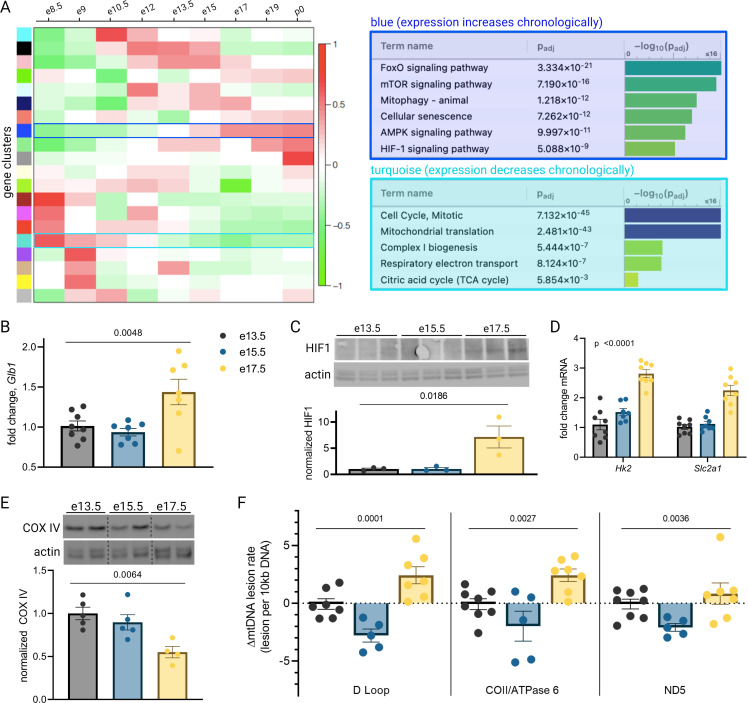
Figure 2. Mouse placental aging is characterized by cellular senescence, hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) signaling, and mitochondrial dysregulation.
Weighted gene correlation network analysis (WGCNA) yielded 20 gene clusters. Functional pathways overrepresented in clusters found to increase (blue) and decrease (turquoise) across gestation highlight enhanced cellular senescence, increased HIF-1 signaling, and decreased mitochondrial synthesis and respiration late in pregnancy (A). mRNA expression of senescence marker Glb1 peaks at e17.5 (B; one-way ANOVA p=0.0048). HIF-1 protein abundance is higher at e17.5 versus e13.5 and e15.5 (C; one-way ANOVA p=0.019), as is expression of HIF-1 targets Hk2 and Slc2a1 (D; two-way ANOVA p<0.0001 for gestational age factor). (See Figure 2—figure supplement 1 for analysis of gene expression changes across timepoints by placental sex.) Mitochondrial abundance, reflected by COX IV protein, decreases with gestational age (E, one-way ANOVA p=0.0064), and mitochondrial DNA lesion rate peaks at e17.5 in the regions of the D-loop (one-way ANOVA p=0.0001), COII/ATPase6 (p=0.0027), and ND5 (p=0.036) (F). (B–F) Each data point represents a biological replicate (e.g. RNA, protein, or DNA extracted from an individual placenta, in turn collected from one of 2–4 pregnant dams per group). Data normalized to mean at e13.5. See Figure 2—source data 1 for uncropped blots.
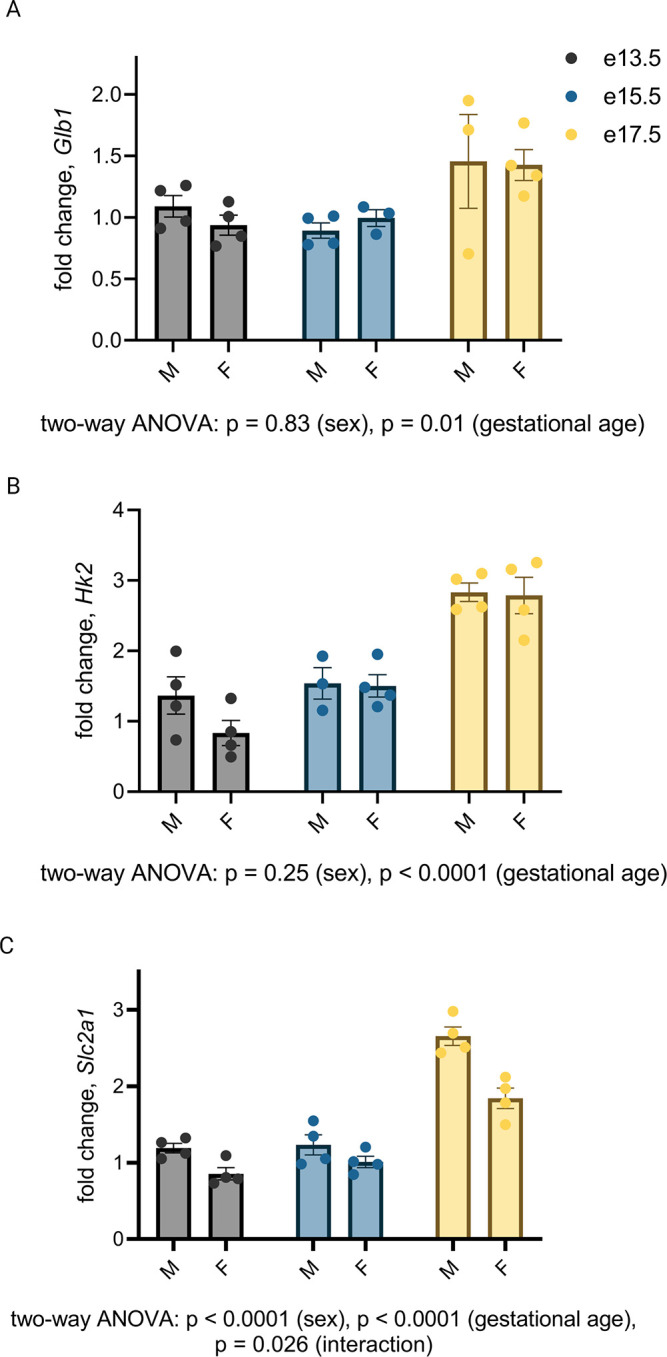
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Gestational age-dependent variability in expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (Hif-1) target Slc2a1, but not Hk2, is affected by placental sex.