Fig. 8.
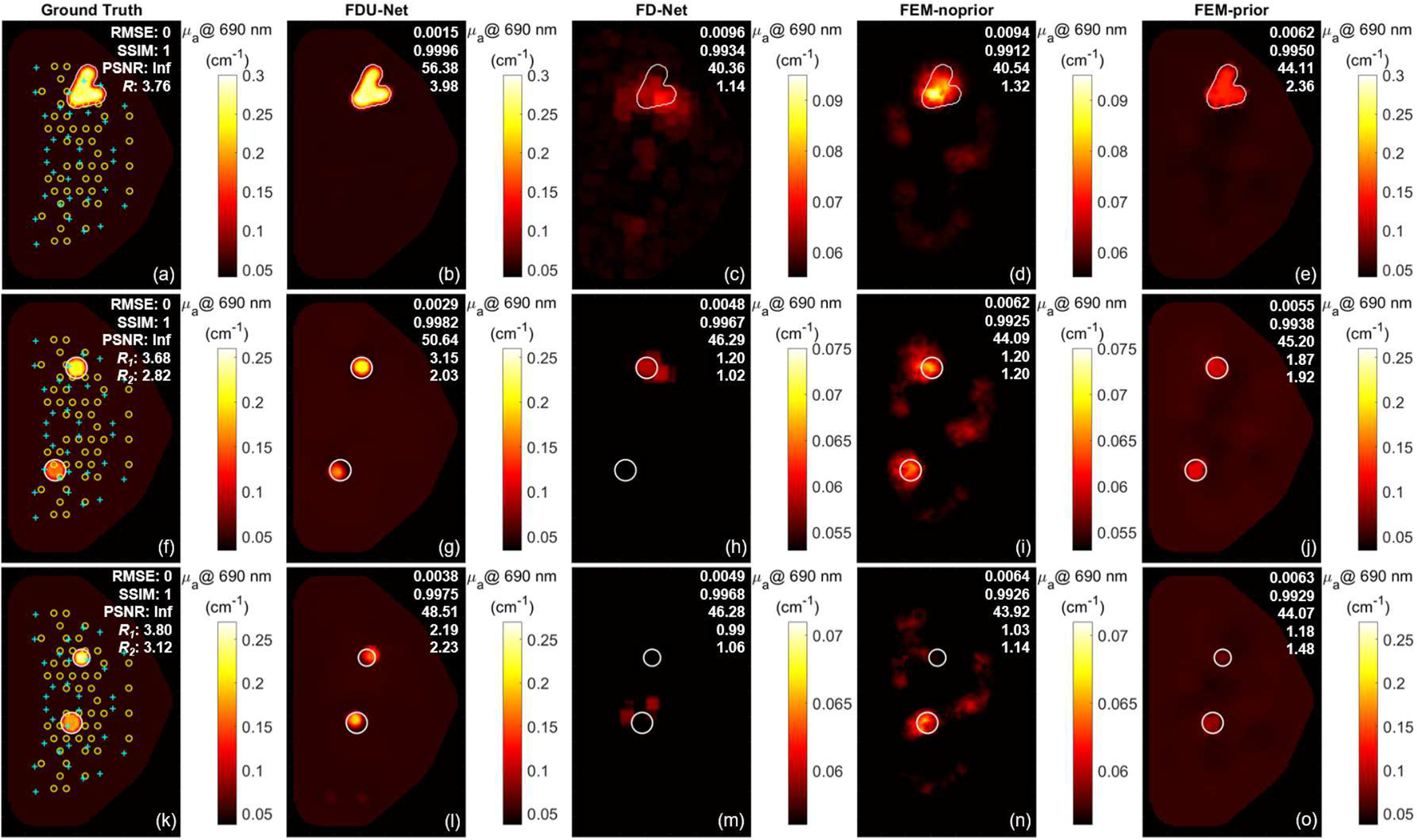
Ground-truth (1st column) and recovered absorption coefficients () at 690 nm using DL-based (2nd column, proposed FDU-Net, and 3rd column, FD-Net) models trained on only singular spherical inclusion cases and conventional FEM-based without (4th column, FEM-noprior) and with (5th column, FEM-prior) structural prior guided reconstruction methods for three previously unseen cases. Top row – a case with an irregularly shaped inclusion; Middle row – a case with two 16-mm diameter spherical inclusions 83.7 mm apart; Bottom row – a case with one 15.7-mm and one 12.4-mm diameter spherical inclusions 52.6 mm apart. RMSE, SSIM, PSNR, and annotated in the top right corner of each reconstructed image from top to bottom. and – Inclusion-to-background ratios for the 1st inclusion on top and a 2nd inclusion on the bottom, respectively, in the two-inclusion cases; Yellow circle – source optode; Cyan cross – detector optode.
