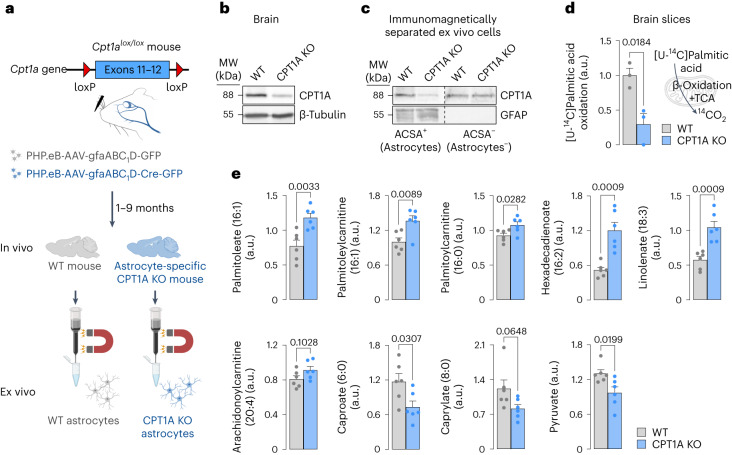
Fig. 1. In vivo astrocyte-specific Cpt1a KO inhibits fatty acid oxidation and alters the metabolomics pattern in the brain.
a, Strategy used to generate astrocyte-specific Cpt1a KO mice and to immunomagnetically purify CPT1A KO astrocytes from adult brain. Created with BioRender.com. b, Western blot against CPT1A protein in astrocyte-specific Cpt1a KO brain. β-Tubulin was used as a loading control; n = 2 mice per condition (Supplementary Fig. 1d). c, Western blotting against CPT1A protein in ACSA+ (astrocytes) and ACSA− (not astrocytes) cells, immunomagnetically isolated from astrocyte-specific Cpt1a KO mouse brain; n = 2 mice per condition. GFAP was used as astrocyte enrichment and loading controls. d, Rate of 14CO2 production from [U-14C]palmitic acid in brain slices of WT and astrocyte-specific Cpt1a KO mice. Data are mean ± s.e.m. P value is indicated (n = 3 biologically independent samples; unpaired Student’s t-test, two-sided). e, Concentrations of a selection of metabolites altered in the metabolomics study of the brain samples from astrocyte-specific Cpt1a KO when compared with WT mice. Data are mean ± s.e.m. P values are indicated (n = 6 mice per condition; unpaired Student’s t-test, two-sided). a.u., arbitrary units.