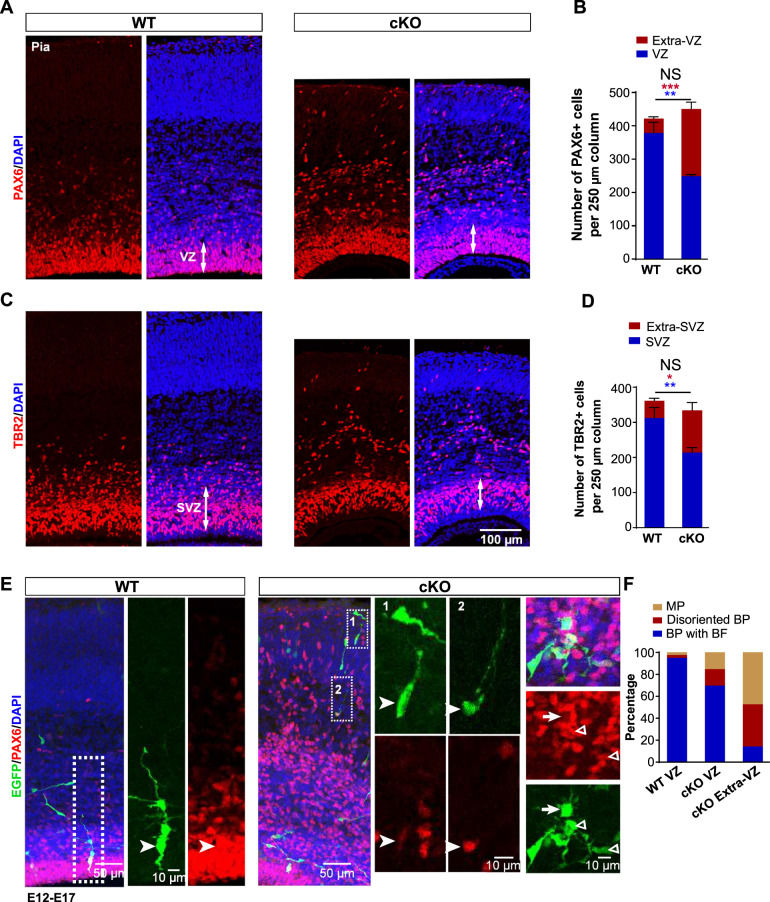
Fig. 2. Arglu1 deletion leads to RG delocalization and detachment from the VZ.
A–D Representative images of cortices stained for PAX6 (A) and TBR2 (C) and quantification of the number of PAX6+ cells (B) and TBR2+ cells (D) in a 250 µm column from E16.5 WT and cKO mice (WT, n = 8; cKO, n = 9 mouse brains). Asterisks indicate significant differences of the number of total PAX6+ or TBR2+ cells (black), in the ventricular zone (VZ, blue), and in the extra-VZ (red) between WT and cKO mice. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, two-tailed Student t test; NS not significant. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. E Representative images of EGFP-expressing cells stained for PAX6 in E17 cortices. Boxed regions are expanded into right panels corresponding to numeric digits. Arrow heads indicate EGFP+ RGs expressing PAX6. Arrow denotes a multipolar RG. Triangles indicate disoriented bipolar RGs. F Quantification of the percentage of EGFP + PAX6+ cells that were multipolar (MP), disoriented bipolar cells (BP) or bipolar with basal process (BP) (WT: VZ, n = 80 cells from four mouse brains; cKO: VZ, n = 66 cells from four mouse brains; Extra-VZ, n = 104 cells from four mouse brains). Note that none of delocalized RGs is an oRG-like cell in morphology.