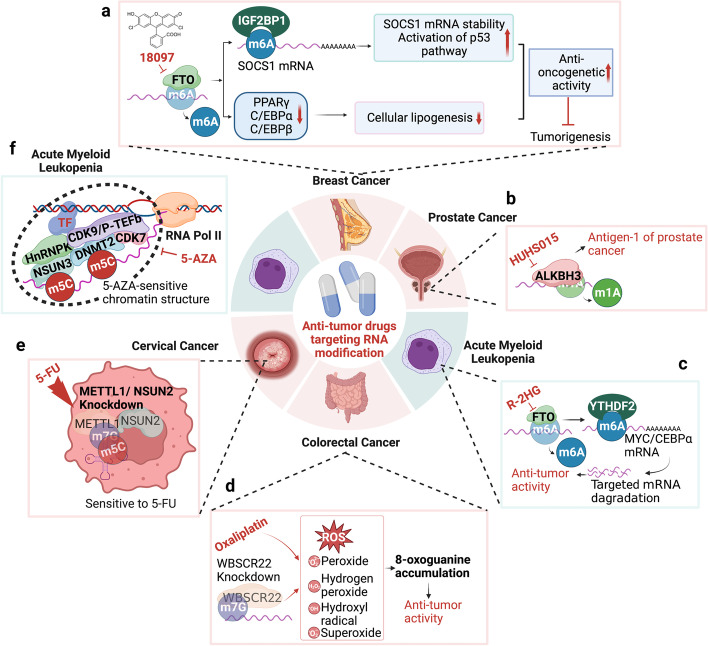
Fig. 4.
Detailed mechanisms of anti-tumor drugs targeting RNA modifications. a 18097 inhibits FTO, thus increasing m6A modification on substrate mRNAs in breast cancer. b HUHS015 disturbs the function of ALKBH3, which serves as a prostate cancer antigen. c R-2HG prevents FTO removal of m6A modification from MYC/CEBPα in AML. d WBSCR22 knockdown enhances the sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells to oxaliplatin. e METTL1/NSUN2 knockdown sensitizes cervical cancer cells to 5-FU treatment. f NSUN3/DNMT2/CDK7/HnRNPK/CDK9/p-TEFb complex binds nascent nuclear RNA, forms a 5-AZA-sensitive chromatin structure in AML