Figure 4.
Splenic B cells from WT and μsKO mice release 11kG and 110 kG EV that contain low molecular weight IgM
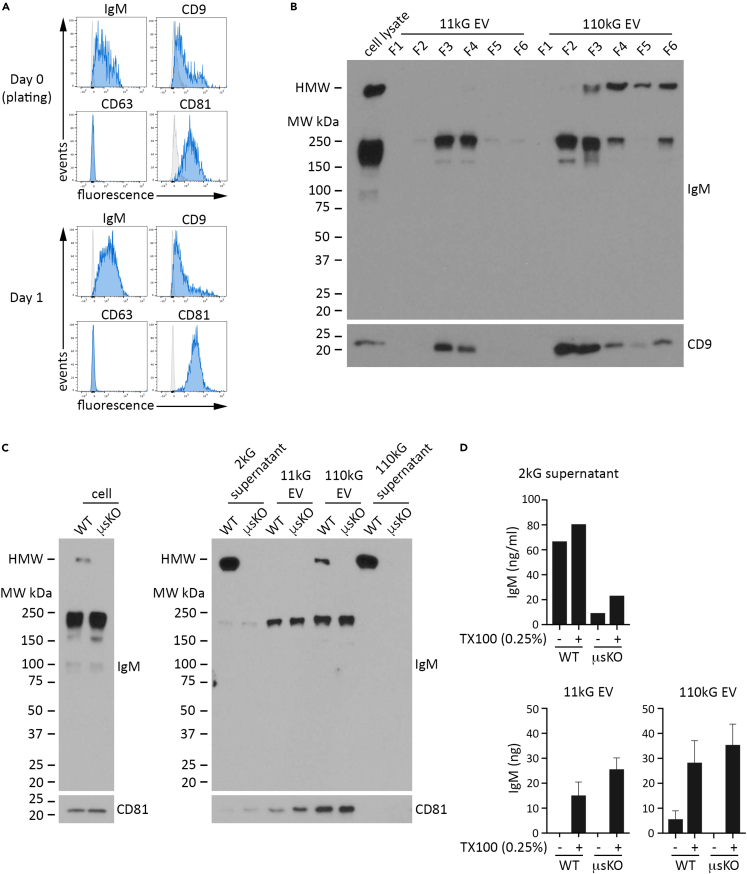
WT mouse splenic B cells were isolated by immunocapture magnetic bead negative selection and cultured unstimulated for 24 h, after which conditioned media was harvested for EV isolation and analysis.
(A) Cell surface expression of IgM, CD9, CD63, and CD81 was determined by flow cytometry at the time of plating (day 0) and at harvest (day 1). Histogram overlays of cells stained for antigen (blue) and corresponding FMO stained cells (gray) are presented.
(B) EV (11kG and 110kG) in day 1 conditioned media were isolated by differential ultracentrifugation (DUC) and then fractionated by sucrose gradient centrifugation. Following buffer wash, each fraction was resuspended in an equivalent volume and then resolved by SDS/PAGE for immunoblot detection of IgM and CD9, as indicated. A sample of day 1 WT splenic B cell lysate (3.75 μg protein) was run as a positive control. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments.
(C) WT and μsKO splenic B cells were isolated by immunocapture magnetic bead negative selection and cultured unstimulated for 24 h, after which conditioned media was collected and cell lysates were prepared. EV were isolated from conditioned media by DUC and resuspended in an equivalent volume of buffer. Equivalent protein (cell lysates; 2 μg) or volume (2kG supernatant, 11 kG EV, 110 kG EV, post-110kG supernatant) for WT and μsKO samples was resolved by SDS/PAGE under unreduced conditions, followed by immunoblot detection of IgM and CD81.
(D) The amount of IgM, as determined by anti-mouse IgM ELISA under buffer and buffer +0.25% TX100 conditions, is shown for 2kG supernatant (top), 11 kG EV (lower left), and 110 kG EV (lower right).
Data in (C) and (D) are representative of two independent experiments. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. See also Figure S4.