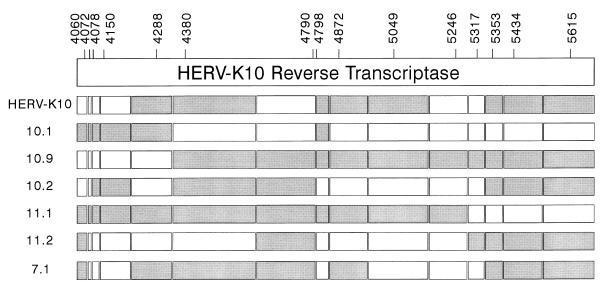
FIG. 10.
Schematic of the mosaic structure of the HERV-K RT gene. The HERV-K RT genes were split in segments around the nucleotides that differ among the isolates. We excluded mutations that were present in a single isolate, thus filtering out potential sequence errors introduced in the RT-PCR amplification protocol. The informative nucleotide positions are indicated at the top. These segments were arbitrarily marked grey or white (e.g., segment 4060 C is white, segment 4060 T is grey). We optimized the genetic linkages, starting at the 3′ end, which may explain the absence of crossover sites in the extreme 3′ RT domain (positions 5353 to 5615).