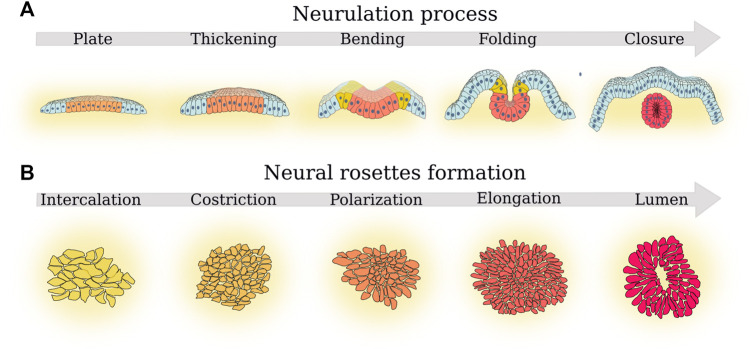
FIGURE 1.
Parallel between the principal phases of neurulation and rosette formation. (A) The five phases of neurulation that determine neural tube morphogenesis (Karzbrun et al., 2021): 1) plate formation, a plate of cells from the ectoderm (light blue cells) became neural ectoderm cells (orange cells); next, 2) in the thickening phase, such neural plate thickens and then start 3) bending. Cells at the border of the neural plate further differentiate becoming neural crest progenitors (yellow cells). In a subsequent 4) folding phase, the margins of the neural plate come together. Finally, 5) in the closure phase, the neural plate completes the folding process and forms the neural tube (red cells). Progenitor crest cells migrate toward other regions of the embryo. (B) The five fundamental cell morphological changes described by Hříbková et al. (2018) during rosette formation. First, 1) cells form confluent layers (cell intercalation) and then 2) such cells tend to form a thicker and more dense layer (cell constriction). Next, 3) cells start forming defects (cell polarization). In the next phase, 4) more cells join the defect (cell elongation) until 5) a lumen is formed in the place of the defect (lumen formation).