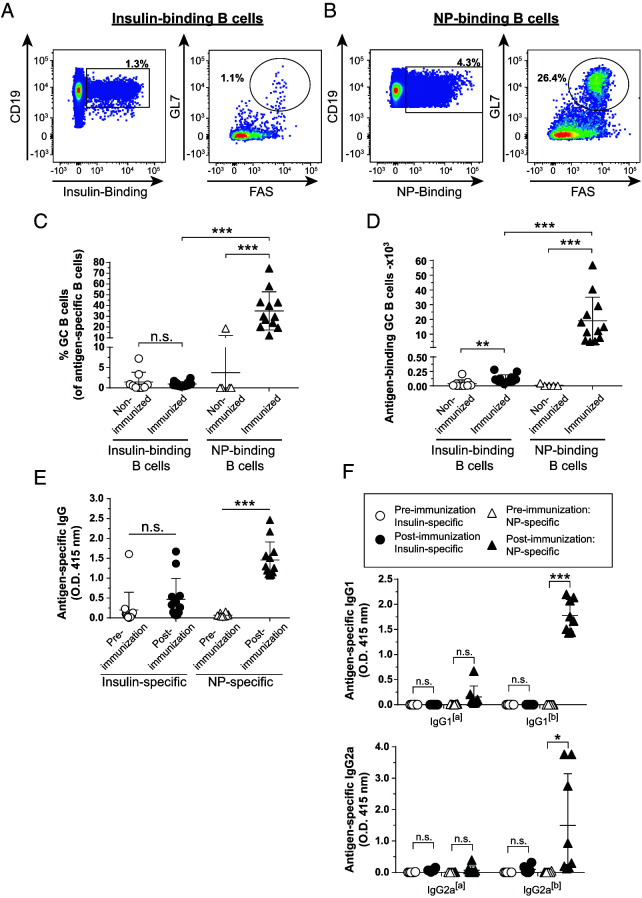
FIGURE 3.
TD immunization with CFA/insulin peptide elicits limited Ab production and GC formation compared with foreign Ag responses in the same VH125SD.NOD mice.
VH125SD.NOD mice were immunized s.c. with both insulin B chain peptide B:9-23 and NP-KLH emulsified in CFA as described in Materials and Methods. Three weeks later, mice were boosted with insulin B chain peptide B:9-23 and NP-KLH emulsified in IFA. Draining medial iliac lymph nodes and sera were collected before immunization or 7 d after boost. (A and B) Representative flow cytometry plots identify GC B cells as in Fig. 1 among insulin-binding (A) and NP-binding B cells (B) in lymph nodes harvested from immunized mice. Frequency (C) or number (D) of Ag-binding GC B cells is shown. The GC B cell frequency is shown for mice that had >20 insulin-binding or NP-binding B cells in the parent B cell gate. Anti-insulin and anti-NP Ab production from both preimmunization and postboost measured in sera by ELISA in VH125SD.NOD mice. (E) Total Ag-specific IgG or (F) allotype-specific Ag-specific IgG1 (top) or IgG2a (bottom) indicates transgenic (IgG1[a] or 2a[a]) or endogenous (IgG1[b] or IgG2a[b]) B cell origin. Ten- to fifteen-wk-old male and female NOD mice. n ≥ 6 mice per group, n ≥ 3 experiments. *p < 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001, two-tailed t test (E and F) or Mann-Whitney U test (C and D).