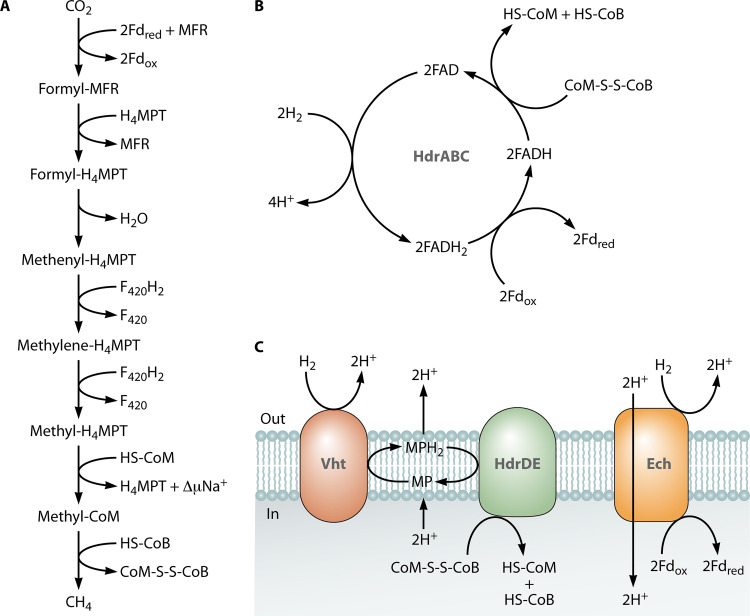
FIG 3.
The CO2-reducing pathway of methanogenesis. (A) The pathway used by all methanogens (with and without cytochromes) that reduce CO2. In Methanosarcinales methanogens, tetrahydrosarcinapterin (H4SPT) may replace tetrahydromethanopterin (H4MPT). (B) Reactions catalyzed by the cytoplasmic, flavin-based, electron-bifurcating heterodisulfide reductase (Hdr) of hydrogenotrophs. The ferredoxin (Fd) reduced in these reactions is used in the initial CO2-reducing step of methanogenesis, rendering methanogenesis a cycle in these organisms. The hydrogenotrophic pathway is known as the Wolfe cycle (195). (C) An example of a membrane-bound electron transport chain found in Methanosarcina spp. MFR, methanofuran; HS-CoM, coenzyme M; HS-CoB, coenzyme B; F420, coenzyme F420; MP, methanophenazine; Vht, methanophenazine-reducing hydrogenase; Ech, energy-converting hydrogenase; FAD, flavin adenine dinucleotide; FADH2, fully reduced form of FAD; FADH, partially reduced flavosemiquinone.