Figure 2.
Inactivation of targeted split IL-4 generates prodrug modules.
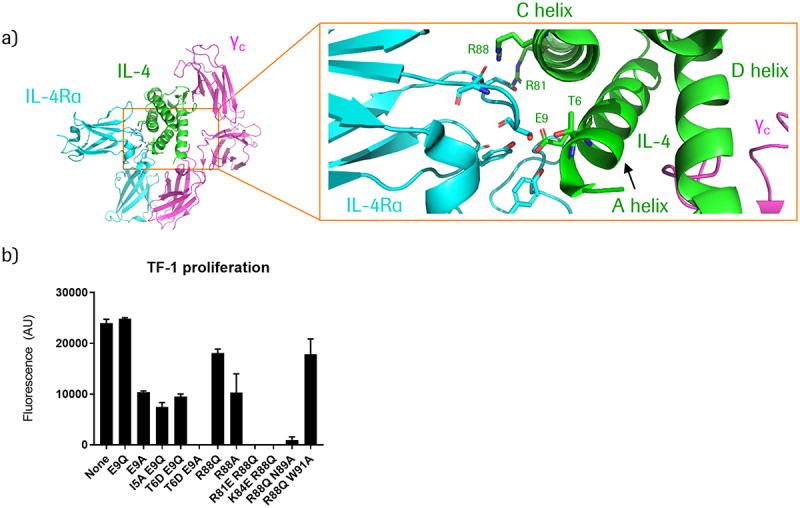
(a) Structural depiction of the IL-4/IL-4Rα/common gamma chain (γC) ternary complex, PDB ID 3BPN.34 Key residues in IL-4 that interact with IL-4Rα are indicated in green. (b) Effect of IL-4 mutations (generated in the context of CD38-targeting 3+1 split IL-4 PACE educts) on IL-4 signaling activity, as measured by proliferation of TF-1 cells treated with 100 nM of the respective molecules. TF-1 cells express CD38 – see following section for more details.
