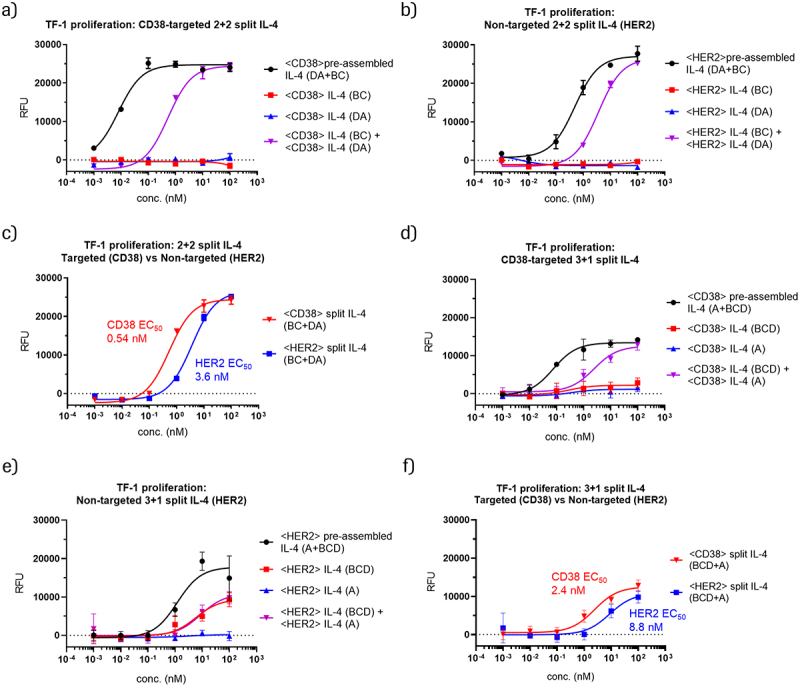
Figure 3.
CD38-targeted IL-4 prodrugs elicit IL-4 cis-signaling and mediate proliferation of CD38-expressing, HER2-negative TF-1 cells.
(a) Proliferation of TF-1 cells after treatment with CD38-targeting prodrugs containing 2+2 split IL-4 or pre-assembled split IL-4. b) Proliferation of TF-1 cells after treatment with non-targeted (HER2-directed) prodrugs containing 2+2 split IL-4 or pre-assembled split IL-4. c) Comparison of TF-1 cell proliferation after treatment with either CD38- or HER2-targeting prodrugs containing 2+2 split IL-4. d) Proliferation of TF-1 cells after treatment with CD38-targeting prodrugs containing 3+1 split IL-4 or pre-assembled split IL-4. e) Proliferation of TF-1 cells after treatment with non-targeted (HER2-directed) prodrugs containing 3+1 split IL-4 or pre-assembled split IL-4. f) Comparison of TF-1 cell proliferation after treatment with either CD38 or HER2-targeting prodrugs containing 3+1 split IL-4.
Figure 3 consists of six panels showing dose-response curves from TF-1 proliferation experiments with various targeted split IL-4 prodrugs and corresponding non-targeted or pre-assembled controls. Panel A shows that individual CD38-targeted 2+2 split IL-4 prodrugs are inactive, while the respective prodrug combination is active. Panel B shows that individual HER2-targeted 2+2 split IL-4 prodrugs, which serve as non-targeted controls on TF-1 cells, are inactive. The respective prodrug combination is active, however with lower potency that the targeted combination in panel A. Panel C shows dose response curves for targeted (CD38) and non-targeted (HER2) prodrug combinations, with the targeted combination being more active than the non-targeted combination. Panels D, E, and F show the same experiments performed in panels A-C, but with 3+1 split IL-4 prodrugs. The dose-response curves indicate inactivity of all prodrugs with the exception of non-targeted (HER2) IL-4 BCD, which shows some residual activity. In panel F, greater activity is observed for targeted (CD38) compared to non-targeted (HER2) prodrug combinations.