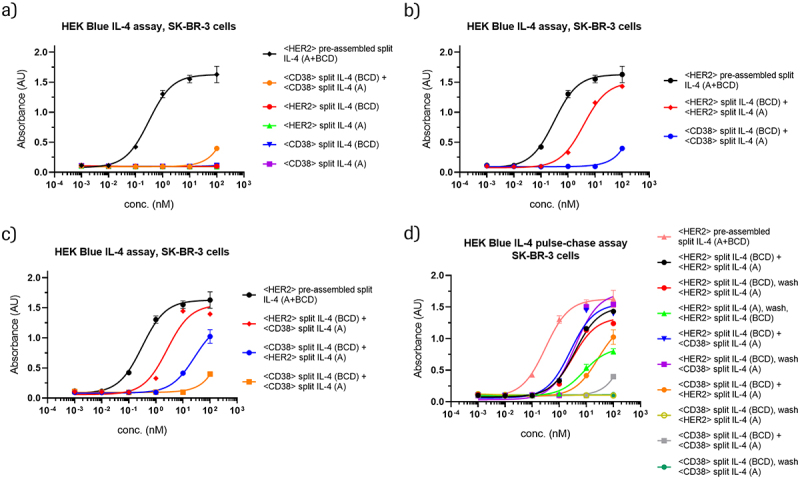
Figure 4.
HER2-binding IL-4 prodrugs assemble on HER2-expressing, CD38-negative SK-BR-3 cells and elicit IL-4 cis- and trans-signaling.
HEK-Blue IL-4 reporter assays reveal activation of HER2-targeted prodrugs, which become activated on HER2-expressing SK-BR-3 cells. For more details about differentiation between cis- and trans-activation in these assays, see Figures S4-S5. Data in panels a-d come from the same experiment. Selected curves are represented in multiple plots for comparison purposes. (a) Individual educts or the combination of non-targeting educts (CD38-targeted) elicit no or only very little IL-4 signaling compared to a pre-assembled HER2-targeted control. (b) The combination of HER2-targeting educts leads to prodrug conversion and IL-4 signaling with a low nM EC50, and approximately two orders of magnitude greater activity compared to non-targeted (CD38) control educts. (c) The combination of one HER2-targeting educt with a complementary non-targeting educt (CD38) can also trigger prodrug conversion and IL-4 signaling. In this setting, relative efficacy depends on the format and composition of the entity that harbors the cell-surface binder. (d) In pulse-chase experiments, one prodrug is added to target cells, followed by a wash step to remove unbound educt before addition of the second prodrug. IL-4 signaling observed upon subsequent addition of complementary non-targeting educts indicates on-cell assembly with the first prodrug, as free prodrugs are removed during the wash step. The fact that removing the first prodrug from the medium does not have a major impact on activity indicates that most of the activation occurs on target cells during the setting of simultaneous addition.
Figure 4 consists of four panels that show dose-response curves from HEK-Blue IL-4 reporter assays with HER2-expressing SK-BR-3 cells. Data from targeted and non-targeted 3 + 1 split IL-4 prodrugs, prodrug combinations, and pre-assembled controls are shown. In panel A, targeted (HER2) and non-targeted (CD38) prodrugs alone show no activity, and the non-targeted prodrug combination shows minimal activity only at the highest concentration. Panel B shows that the targeted prodrug combination (HER2) is markedly more active than the otherwise identical non-targeted combination. Panel C shows that combinations of targeted (HER2) and non-targeted (CD38) prodrugs also elicit activity, with the targeted IL-4 (BCD) plus non-targeted IL-4 (A) combination being more active than the targeted IL-4 (A) plus non-targeted IL-4 (BCD) combination. Panel D shows the results of pulse-chase experiments for different targeted and non-targeted 3 + 1 split IL-4 prodrug combinations, revealing the highest activities when targeted IL-4 (BCD) prodrugs (HER2) are applied before the wash step, combined with either a targeted (HER2) or non-targeted (CD38) prodrug after the wash.