Figure 4. Scope of decarboxylative carbon–heteroatom bond formation.
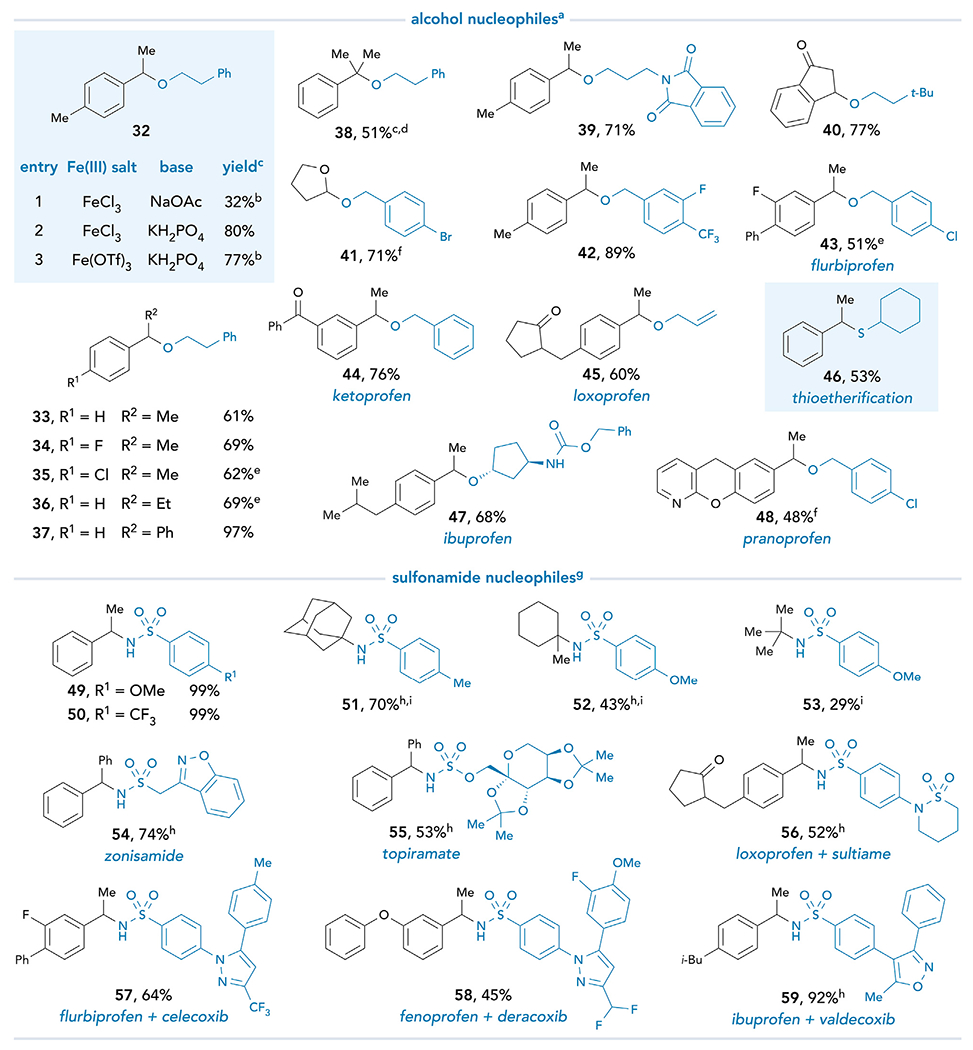
See supplemental information for experimental details. All yields are isolated unless otherwise noted. aReaction conditions for O- and S-nucleophiles: Fe(OTf)3 (3.0 equiv), K2HPO4 (5.0 equiv), nucleophile (3.0 equiv), carboxylic acid (1.0 equiv), and CH2O2 (0.10 M). bYield was determined by 1H NMR analysis of the crude reaction mixture using 1-methylnaphthalene as an internal standard. c1,2-DCE used as the solvent. dFeCl3 used as iron salt. e48 h. fPyridine (3 equiv) used as the base. gReaction conditions for N- nucleophiles: FeCl3 (3.0 equiv), Na3PO4 (3.0 equiv), nucleophile (3.0 equiv), carboxylic acid (1.0 equiv), and CH2O2 (0.10 M). hFe(OTf)3 used as the iron salt. iNaOAc used as the base.
