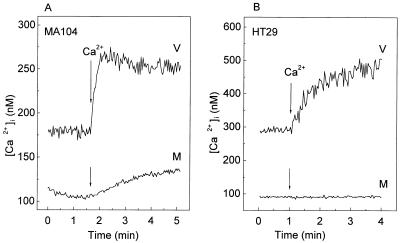
FIG. 2.
Increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration and plasma membrane permeability to Ca2+ in rotavirus-infected MA104 and HT29 cells. At 7 h postinfection, MA104 (A) and HT29 (B) monolayers were trypsinized, and cell suspensions were loaded with fura-2 for the measurement of [Ca2+]i (see Materials and Methods). Permeability to Ca2+ in rotavirus (V)- or mock (M)-infected cells was evaluated by the change in [Ca2+]i induced by the addition of 5 mM CaCl2 to the extracellular medium (arrow), which initially contained 1 mM Ca2+. Results of a representative experiment of a series of three for each cell type are shown.