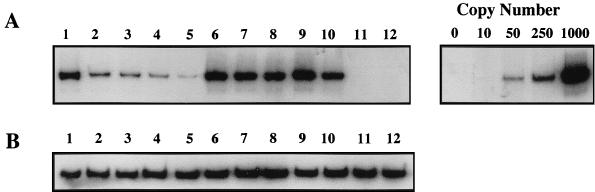
FIG. 7.
Cyclin-dependent kinases do not complement reverse transcription defects associated with Δtat viruses. (A) Viral supernatants from 293 cells producing Δtat virus (lanes 1 to 5) or wild-type HIV-1 (lanes 6 to 10) following transfection of wild-type tat (lanes 1 and 6), an empty RSV expression vector (lanes 2 and 7), a wild-type cdk7 expression vector (lanes 3 and 8), a wild-type cdk9 expression vector (lanes 4 and 9), a wild-type cdc5 expression vector (lanes 5 and 10), mock supernatant (lane 11), or heat-inactivated wild-type HIV-1 (lane 12) were used to infect 5 × 106 activated PBMCs. At 2 h postinfection, residual virus was removed by washing, and Hirt lysates were prepared at 24 h postinfection. The recovered nucleic acids were assayed for HIV-1 negative-strand strong-stop DNA. (B) Quantitative PCR analysis of Cyt-OxyII content in Hirt lysates was used to standardize the DNA recovery. All PCRs were performed within the linear range as determined by assays of HIV-1 DNA copy number (0, 10, 50, 250, and 1,000). This analysis is representative of PCRs performed for three separate HIV-1 infections with independently prepared virus stocks.