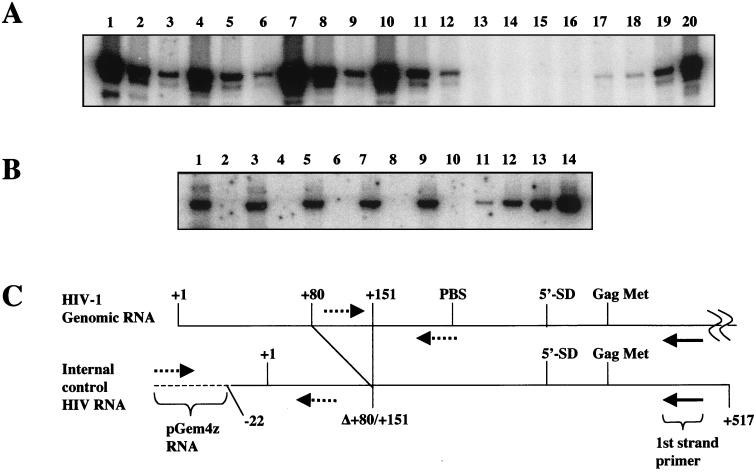
FIG. 8.
Analysis of genomic RNA packaging. (A) Supernatants containing wild-type virus (lanes 10 to 12), Δtat virus (lanes 1 to 3), or Δtat virus complemented with wild-type tat (lanes 7 to 9) or [E2G, D5G, E9G] (lanes 4 to 6) or mock complemented (lanes 13 to 16) were pelleted through 20% sucrose and suspended in PBS-BSA buffer. An IC RNA was added to purified virus that contained 100 ng of p24 Ag, and both RNAs were copurified. cDNA reactions were performed in either the presence or absence of M-MLV with a first-strand primer that annealed to sequences located downstream from the Gag initiating methionine shown in panel C. The cDNA was serially diluted in fivefold increments and assayed by PCR for HIV-1 DNA with primers indicated in panel C. PCRs were performed on HIV-1 DNA present at 0, 101, 102, 103, and 104 copies (lanes 16 to 20). (B) The RNA recovery and cDNA synthesis were similar for each cDNA reaction corresponding to Δtat (lanes 1 and 2), Δtat plus [E2G, D5G, E9G] (lanes 3 and 4), Δtat plus wild-type tat (lanes 5 and 6), wild-type virus (lanes 7 and 8), and mock virus (lanes 9 and 10). IC RNA was reverse transcribed in either the presence (lanes 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9) or absence (lanes 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10) of M-MLV and detected by PCR with the primers shown in panel C (dotted lines). IC plasmid DNA standards present at 20, 100, 300, and 1,000 copies are shown (lanes 11 to 14). (C) Model showing HIV-1 RNA and IC RNA. An internal deletion from +80 to +151 in IC RNA allows detection of IC cDNA from HIV-1 cDNA by PCR with the indicated primers. Solid arrow, first-strand cDNA primer; dotted arrows, PCR primers; dotted line, pGem4Z RNA; solid line, HIV-1 RNA.