Figure 2.
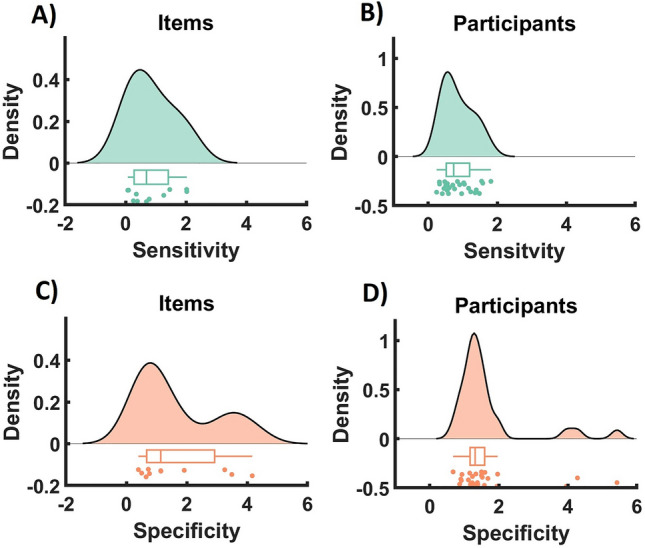
Sensitivity and specificity of interventions across items and participants. (A, B) Sensitivity is defined by the normalized changes in the responses (Methods, Eq. 2). Positive values indicate a change in the expected direction i.e., when the intervention was meant to reduce the rating, the subsequent rating after the intervention was indeed reduced and when the intervention was meant to increase the rating, the subsequent rating was indeed increased. (C, D) Specificity is defined by the relative absolute change of the intervened item compared to the average change of all the other items (Methods, Eq. 3). All specificity values are positive and higher values (of more than 1) indicating that perturbed items change more than the average of the other 10 items.
