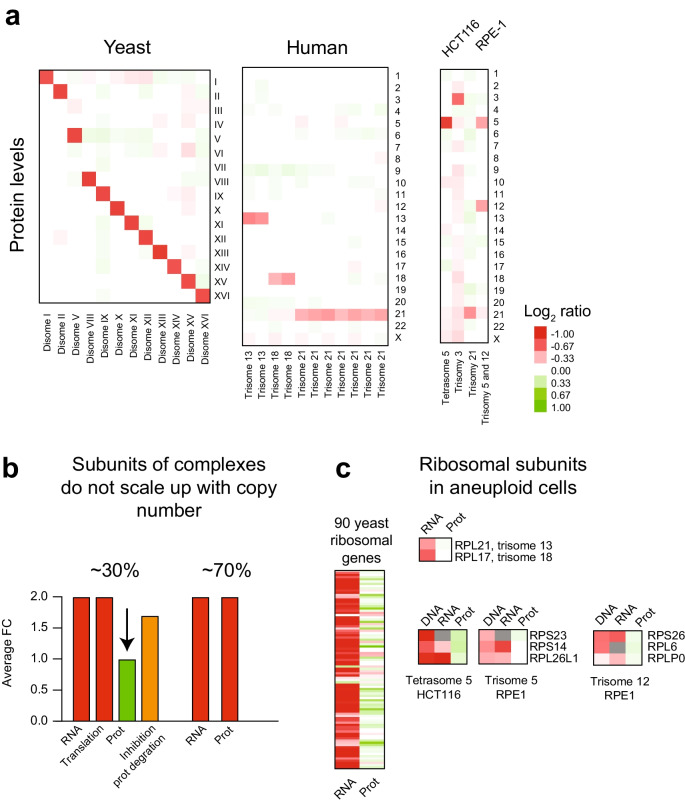
Fig. 3.
Protein levels increase proportionally to gene copy number in aneuploid cells, except for subunits of multiprotein complexes. a Heatmap of the average log2 ratio of protein levels per chromosome in aneuploid cells relative to controls. Proteomics data for yeast was obtained from Dephoure et al. (Dephoure et al. 2014), human trisomies from Hwang et al. (Hwang et al. 2021), and human cell lines from Stingele et al. (Stingele et al. 2012). b About 30% of duplicated proteins enriched for subunits of multiprotein complexes do not scale up with gene copy numbers in yeast and human aneuploid cells (green bar). Ribosome footprinting in yeast disomes shows that the attenuated proteins are translated proportionally to gene copy number. Inhibition of protein degradation leads to increased levels of the attenuated proteins within 90 s (orange bar). c Heatmaps of mRNA levels and protein levels of duplicated ribosomal subunits in yeast and aneuploid human cell lines are shown. This gene set invariably shows increased transcript levels, but the proteins are degraded—color scale bar of log2 ratio is the same as in a