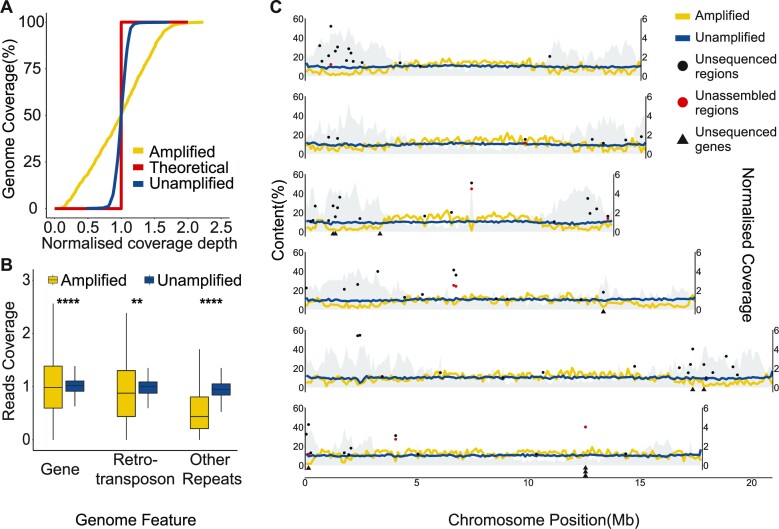
Figure 1.
Sequencing coverage of C. elegans genomic DNA. (A) Cumulative genome coverage versus the genome-wide median. The red line indicates the theoretical coverage of unbiased coverage. More deviation away from this line suggests less uniformity across the genome. (B) Normalized read coverage on genes and repeats. Repeats were categorized into two groups: retrotransposons and other repeats. Retrotransposons include long interspersed nuclear elements (LINEs), short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) and long terminal repeats (LTRs). DNA transposons, RC Helitron, rRNA, snRNA, tRNA, satellite, simple repeat and unknown repeats were together labeled as other repeats. **P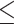 0.01, ****P
0.01, ****P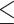 0.0001. (C) Lines represent normalized read coverage of amplified and unamplified data. The black and red dots represent the top 10% of regions (11.1–44.8 kbp and 10.1–54.5 kbp) that were not sequenced and not assembled. The triangles represent the position of genes that were not sequenced at all. The shaded area indicates the proportions of repeats along the chromosomes.
0.0001. (C) Lines represent normalized read coverage of amplified and unamplified data. The black and red dots represent the top 10% of regions (11.1–44.8 kbp and 10.1–54.5 kbp) that were not sequenced and not assembled. The triangles represent the position of genes that were not sequenced at all. The shaded area indicates the proportions of repeats along the chromosomes.