Fig. 3.
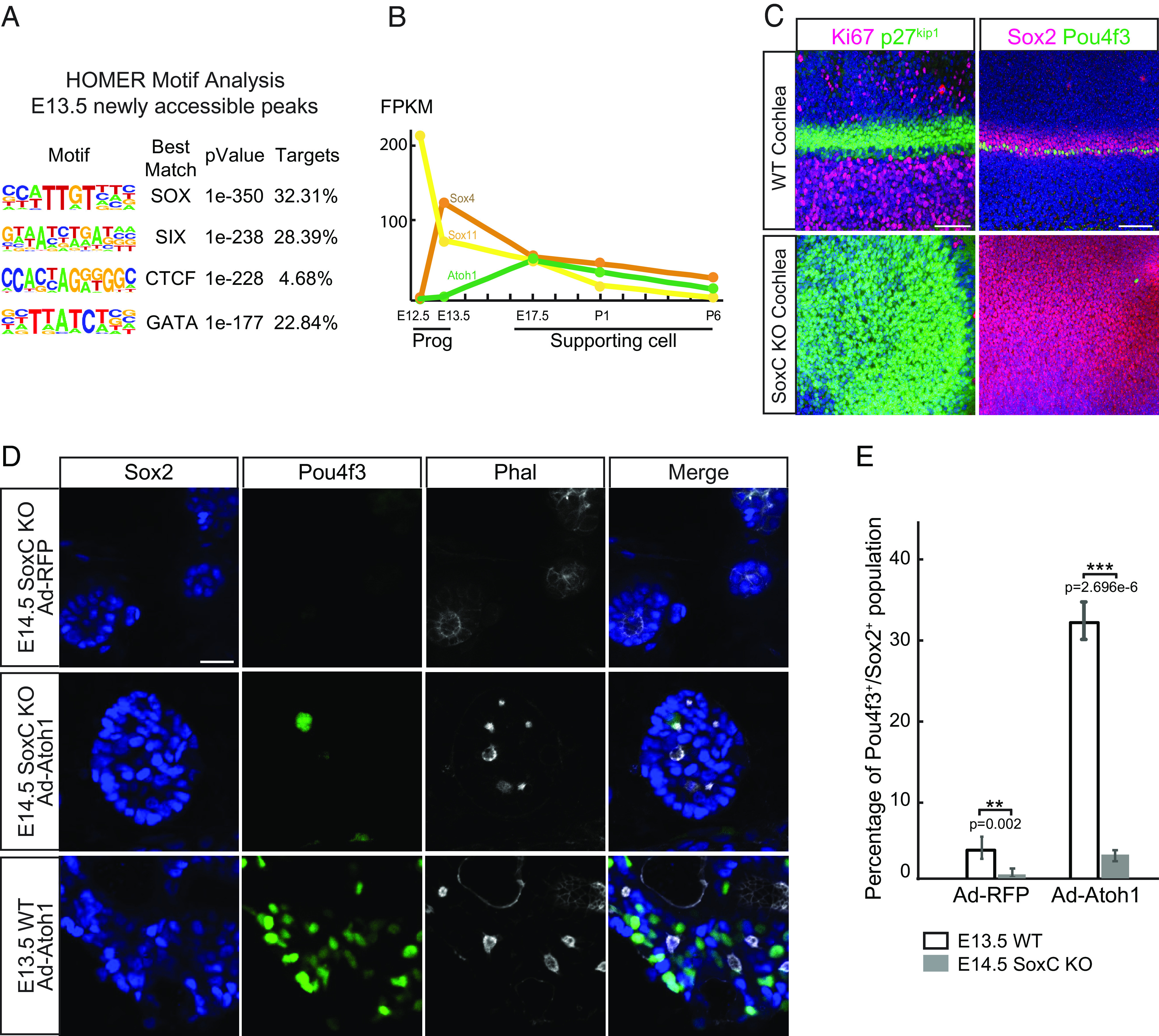
SoxC transcription factors are essential for initiation of sensory differentiation during organ of Corti development. (A) HOMER motif analysis shows top four most enriched DNA-binding motifs in E13.5 newly accessible chromatin regions. (B) Gene expression in fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads (FPKM) for Sox4, Sox11, and Atoh1 is demonstrated in E12.0 and E13.5 progenitors (Prog) and E17.5-P6 supporting cell (SC) (n = 2 for Progs, n = 3 for SCs). Note that Sox4 expression is significantly up-regulated in E13.5 progenitors prior to the onset of Atoh1 expression. (C) Representative immunofluorescent images show the whole cochleae isolated at E14.5 from the WT and SoxC cKO littermate embryos. Ki67-positive (magenta) proliferating cells and the p27kip1-positive (green) postmitotic progenitor cells (Left) are labeled. Note that progenitor cell cycle exit is not affected in the SoxC cKO organs. Sox2-positive supporting cells (magenta) and one row of Pou4f3-positive inner hair cells (green) are detected in the WT but not in the SoxC cKO organs. Cell nuclei are labeled with DAPI (blue). (Scale bar, 100 μm.) (D) Representative immunofluorescent images show dissociated cochlea cells isolated at E14.5 from the SoxC cKO and WT mice littermates, infected with Ad-RFP control or Ad-Atoh1-RFP virus, and maintained in culture for 3 d. Actin is labeled by Phalloidin (white), hair cells are labeled with Pou4f3 (green), and supporting cells are labeled by Sox2 (blue). Note that although the cells are organized into the sensory rosettes, Atoh1 overexpression fails to induce Pou4f3-positive hair cells (green) in absence of SoxC. (Scale bar, 20 μm.) (E) Bar graph shows quantitative analysis of the cultures in D. Compared to the WT cultures, the percentage of hair cells is significantly decreased in the SoxC cKO cultures transduced with either Ad-RFP or Ad-Atoh1-RFP virus (n = 3 for each condition).
