Fig. 5.
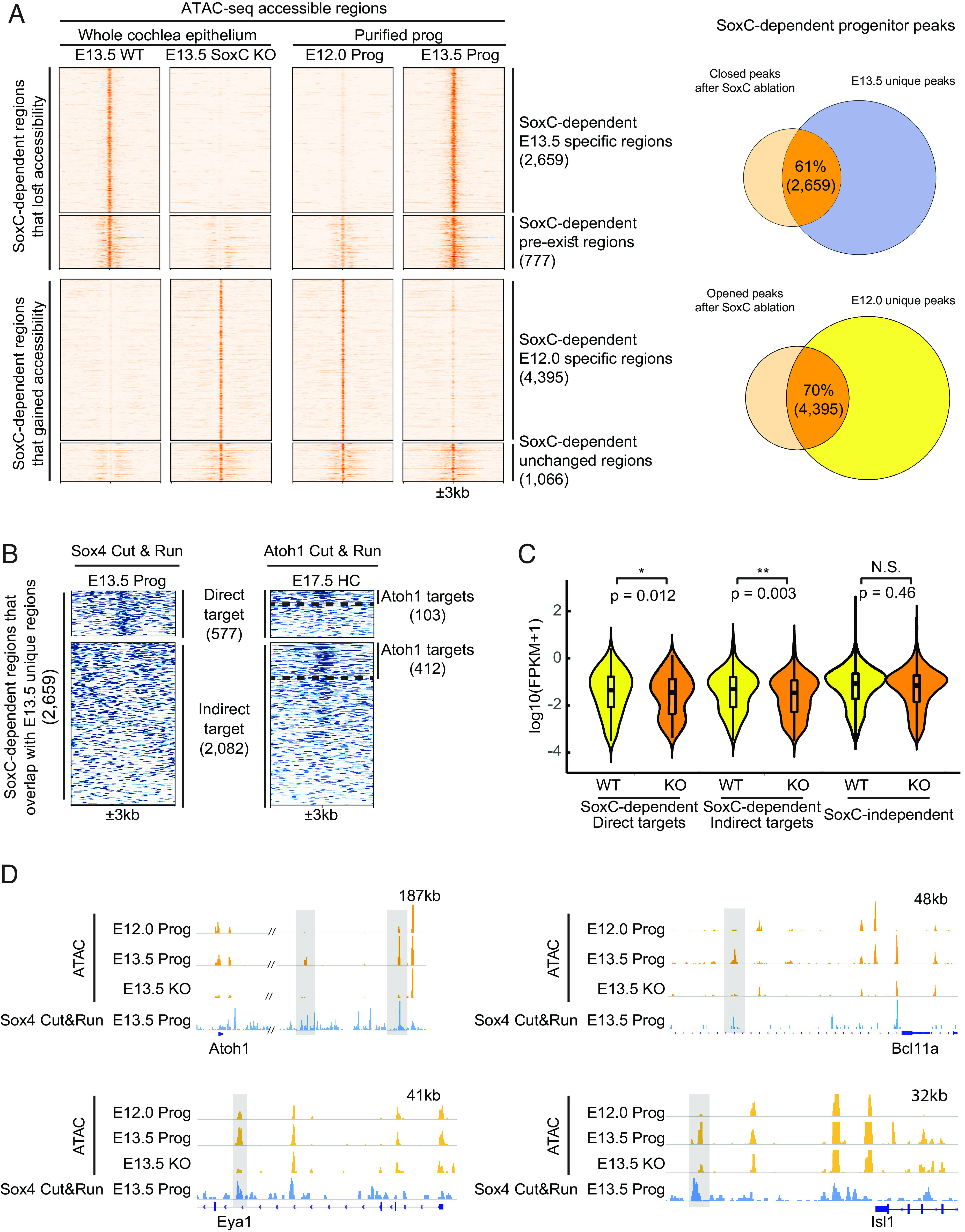
SoxC transcription factors control chromatin accessibility to promote hair cell differentiation in the E13.5 organ of Corti. (A) Heatmap shows accessible genomic regions identified by ATAC-seq in the SoxC cKO cochlea at E13.5 in relation to the E12.0 and E13.5 progenitor cell peaks. Among all the SoxC-dependent peaks, 2,659 that lose accessibility in the SoxC cKO cochlea overlap with E13.5 newly emerged regions; 4,395 peaks that gain accessibility in the SoxC cKO overlap with E12.0 progenitor–specific regions that are closed at E13.5. Scale of each sample column is ±3 kb from the center of the peaks. Venn diagrams on the right show numbers and percentages of the overlap between SoxC-dependent genomic regions and E13.5 (Upper) or E12.0 (Lower) unique progenitor peaks. (B) Heatmap shows direct and indirect Sox4 targets identified using ChIP-seq (Sox4 Cut&Run) in E13.5 progenitors. Twenty-two percent (577) of the E13.5 newly opened SoxC-dependent progenitor peaks (2,659) are direct targets of Sox4. Atoh1 Cut&Run on the right demonstrates the genomic loci bound by Atoh1 in E17.5 hair cells (HC): 103 SoxC-dependent peaks are both Sox4 and Atoh1 direct targets, 412 indirect Sox4 targets are directly bound by Atoh1. Dotted lines separate direct/indirect targets of Atoh1. (C) Violin plots show the expression changes [log10(FPKM+1)] of genes associated with SoxC-dependent (577 direct targets and 2,082 indirect targets demonstrated in panel B) and SoxC-independent (88,674 peaks common in between WT and KO) regulatory elements in WT and SoxC cKO progenitor cells (scRNA-seq datasets). Genes associated with SoxC-dependent regulatory elements are significantly down-regulated, while genes associated with SoxC-independent regulatory elements are not significantly changed upon SoxC ablation. (D) IGV tracks show ATAC-seq profiles (orange) and Sox4 Cut&Run profile (blue) of representative genomic loci for key sensory lineage genes (Atoh1, Bcl11a, Eya1 and Isl1). The putative enhancers highlighted in gray boxes, gain accessibility in E13.5 progenitors (Prog), lose their accessibility upon SoxC ablation, and are bound by Sox4 transcription factor.
