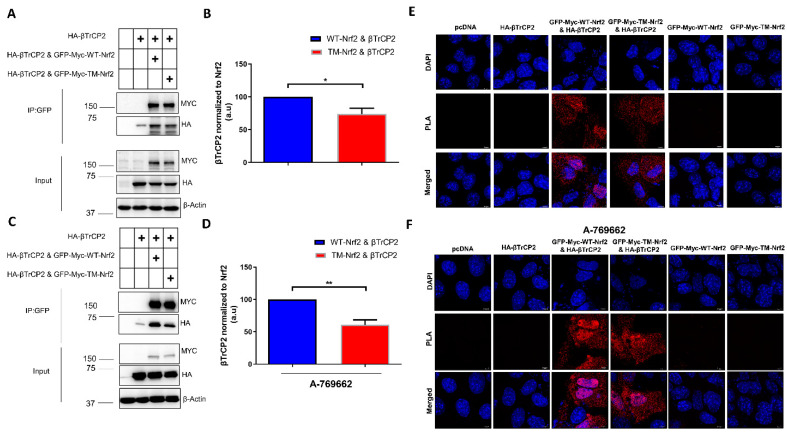
Figure 2.
Mutation of the AMPK-dependent phospho-sites to alanine impedes the interaction of Nrf2 with β-TrCP2 in Keap1−/− cells. (A–D) Keap1-null MEFs were transfected with an expression plasmid for HA-tagged β-TrCP2 alone or together with constructs encoding EGFP-MYC-WT-Nrf2, the triple mutated version EGFP-MYC-TM-Nrf2, or pcDNA as indicated for 48 h followed by the absence (A,B) or presence (C,D) of the AMPK activator A769662 (50 μM, 4 h). Cells were also treated at the same time with MG132 (10 μM, 4 h) to stabilize Nrf2, which was pulled down using GFP-Trap. Precipitated proteins, as well as input controls, were immunoblotted for MYC, HA, and β-Actin. Representative blots (A,C) and quantification analysis (B,D) of 3 independent experiments are depicted. Plus symbols in the tables indicate the different constructs/chemicals used in the various experimental conditions. (E,F) Keap1-null MEFs were transfected with (i) pcDNA, (ii) HA-tagged β-TrCP2, or co-transfected with (iii) HA-tagged β-TrCP2 and EGFP-MYC-tagged WT-Nrf2, (iv) HA-tagged β-TrCP2 and EGFP-MYC-tagged TM-Nrf2 expression plasmids, or (v) EGFP-MYC-tagged WT-Nrf2 and (vi) and EGFP-MYC-tagged TM-Nrf2 alone, and then treated with MG132 (10 μM) for 4 h in the absence (E) or presence (F) of the AMPK activator A769662 (50 μM, 4 h). Cells were fixed with 4% Paraformaldehyde and subjected to PLA. Data are presented as means ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t-test, * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01.