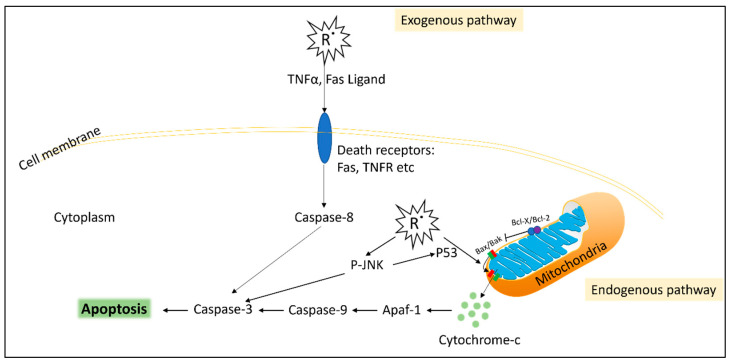
Figure 1.
Simplified diagram of reactive oxygen species (R˙)-induced apoptosis. Exogenous pathway: Free radicals induce death receptors such as the TNF receptor (TNFR) or FAS receptor, as well as inducing the production of their ligands TNFα and FasL (respectively) from neighbouring cells. The death receptors stimulate caspase-8, which activates apoptosis. Intrinsic pathway: cellular free radicals, such as H2O2, result in mitochondrial dysfunction via the Bax/Bak leaking of cytochrome-c from the mitochondria, which activates apoptosis via the caspase complex. Cellular free radicals also result in the phosphorylation of JNK (P-JNK) and P53, which leads to further activation of apoptosis.