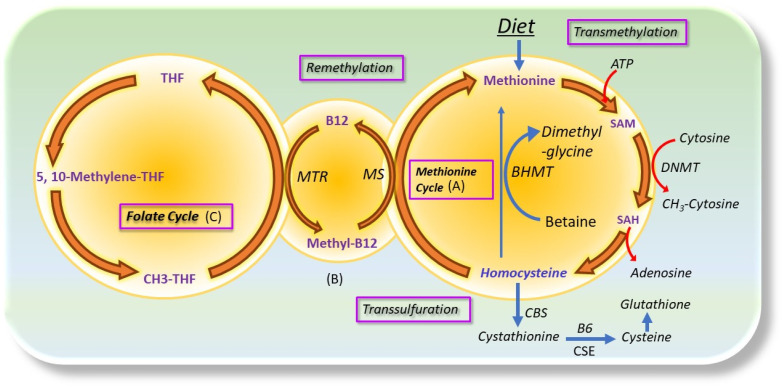
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of Hcy production through the methionine and folate cycle. (A) Dietary methionine is converted to homocysteine (Hcy) through S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) and S-adenosyl homocysteine (SAH) and then back to methionine (MET) via the remethylation pathway. Half of Hcy goes to the transsulfuration pathway, where it is converted to cysteine with the help of cystathionine-β synthase (CBS) and cystathionine-γ lyase (CSE). Then cysteine is further converted to glutathione (GSH); (B) Conversion of cobalamin (vitamin B12) to methyl-B12 in the presence of methionine synthase reductase (MTR) is necessary for remethylation of 5-methyl-tetrahydrofolate (THF) to THF; (C) Dietary folic acid (vitamin B9) enters the folate cycle after its conversion first to dihydrofolate (DHF) and then to THF. The 5, 10-methyltetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) is a key enzyme that converts 5, 10-methylene-THF to 5-methyl-THF [15].