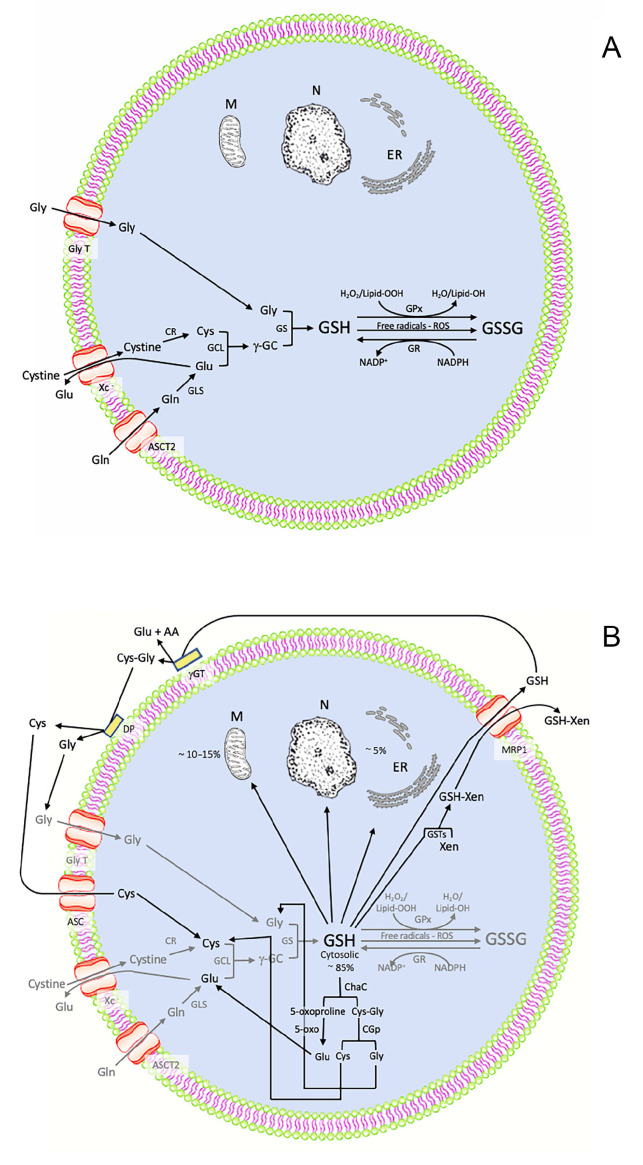
Figure 2.
(A) Biosynthetic pathway and antioxidant role of GSH and its interconversion into the oxidized form GSSG. (B) Intracellular distribution, degradation pathways, and recycling of GSH. GSH = glutathione; N = nucleus; M = mitochondrion; ER = endoplasmic reticulum; Gln = glutamine; Glu = glutamic acid; Cys = cysteine; Gly = glycine; Gly T = glycine transporter; Xc- = cystine/glutamate antiporter; ASCT2 = Alanine/serine/cysteine transporter 2; GLS = glutaminase; γ-GC = γ -glutamyl-cysteine; GCL = glutamate-cysteine ligase; GS = glutathione-synthetase; GPx = glutathione peroxidase; GSSG = glutathione disulfide; GR = glutathione reductase; Cys-Gly = cysteine–glycine; ASC = Alanine/serine/cysteine transporter 1; MRP1 = multidrug-resistant protein 1; GSTs = glutathione S-transferases; Xen = xenobiotics; GSH-Xen = glutathione plus xenobiotics; γ-GT = γ-glutamyl transferase; DP = Cysteinyl glycine dipeptidase; ChaC = glutathione-specific gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase; CGp = Cys-Gly peptidase; 5 oxo = 5-oxoprolinase.