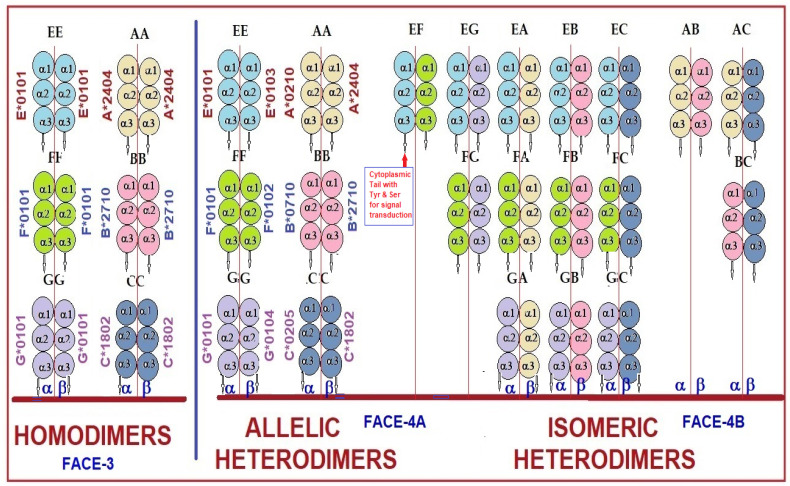
Figure 4.
Diagrammatic illustration of different combinations of dimers of peptide-free (implying unfolded) monomeric B2m-free HCs (Face-2) resulting in different kinds of peptide-free (implying unfolded) allelic homodimers (Face-3), peptide-free (implying unfolded) allelic heterodimers (Face-4A), and peptide-free (implying unfolded) isomeric heterodimers (Face-4B). For the purpose of illustrating a similarity with HLA-II, we have suggestively and tentatively indicated one monomer as α chain and another monomer as β chain, although in reality both of them are α chains. As defined and designated by IMGT labels (Lefranc et al. [3]), each HC, though considered unfolded, may consist of groove (G)-like domains (α1 [D1] and α2 [D2]) and a constant (C)-like domain (α3 [D3]) with cytoplasmic tail. Domains of different alleles of different isomers or the α and β chains as shown in the figure may vary extensively. This implies that the ligands binding to the α1 domain of these two chains may differ markedly. More structural studies on the dimers may further clarify the G and C domains of each chain in a homodimer and in the allelic and isomeric heterodimers.