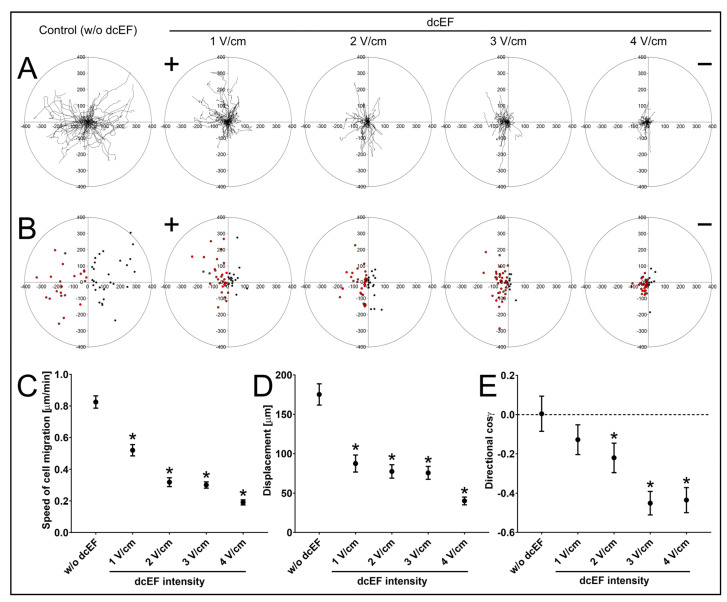
Figure 1.
Migration of NA HBF in isotropic conditions and an electric field of physiological magnitude. (A) Composite trajectories of NA HBF migration both without and in the presence of a direct current electric field (dcEF) of physiological magnitude (1–4 V/cm) are shown as circular diagrams. The initial point of each trajectory was moved to the origin of the coordinate system. Each trajectory was created using 48 points of cell centroids recorded at 10-minute intervals for 8 h. The positive electrode (anode) of dcEF (if present) is located on the left side. Scale in μm; n = 50 cells per condition. (B) Final positions of NA HBF migration plotted on the coordinate system. dcEF (if present) is oriented as previously. Points located on the left (anodal) side of the 0Y axis are marked in red, while points located on the right (cathodal) side of the 0Y axis are marked in black. Scale in μm; n = 50 cells per condition. (C–E) The quantitative parameters of NA HBF migration both without and in the presence of dcEF. (C) Speed of cell migration; (D) cell displacement; (E) directionality of cell migration. Values are calculated as the mean value for the analysed population ± SEM (n = 50); * statistically significant values relative to those of control (p < 0.05).