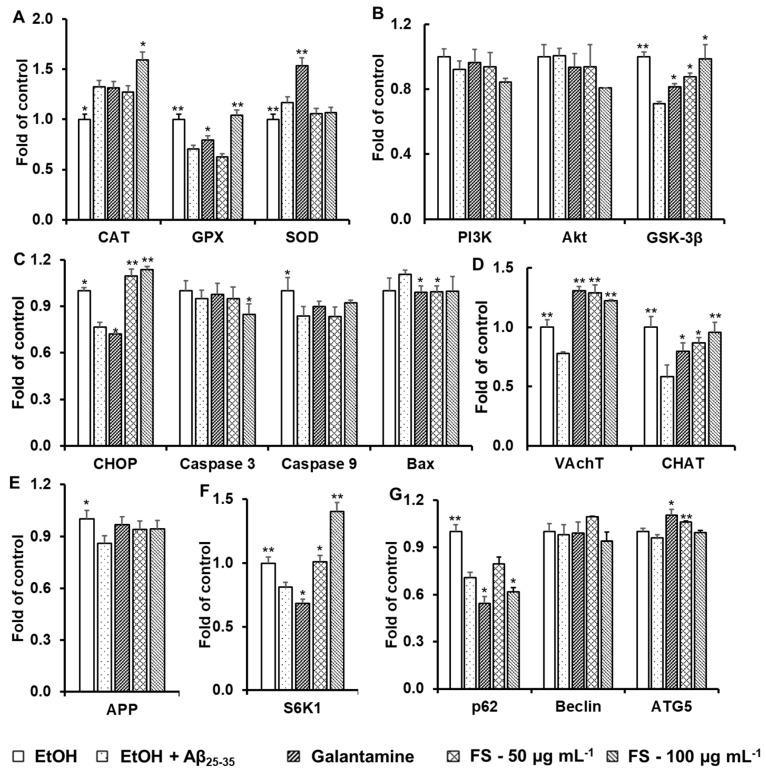
Figure 6.
Effect of fucoxanthin on the expression of genes related to antioxidant enzymes (A), PI3K/Akt signaling (GSK-3ß) (B), the ER pathway (C), the biosynthesis of ACh (D), proteolytic processing (E), modulating protein translation (F), and autophagy (G) in C6 cell lines. The expression levels of genes were assessed with quantitative real-time PCR and normalized to β-actin in cells stimulated with fucoxanthin (concentrations of 50 and 100 µg mL−1) or galantamine (concentration of 0.1 μg mL−1) for 24 h prior to 20 mM Aβ25–35 exposure for 1 h. EtOH was used as control. The data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 3). Significant differences in the cell damage induced by Aβ25–35 are denoted by * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.001. EtOH: ethanol; SOD: superoxide dismutase; CAT: catalase; GPx: glutathione peroxidase; PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinase; Akt: protein kinase B; GSK-3β: glycogen synthase kinase 3β; CHOP: CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous protein; Bax: Bcl2-associated X; CHAT: choline acetyltransferase; VAChT: vesicle acetylcholine transporter; APP: amyloid precursor protein; S6K1: S6 kinase 1; p62: sequestosome-1/A170/Zeta-interacting protein; ATG 5: autophagy-related gene 5.