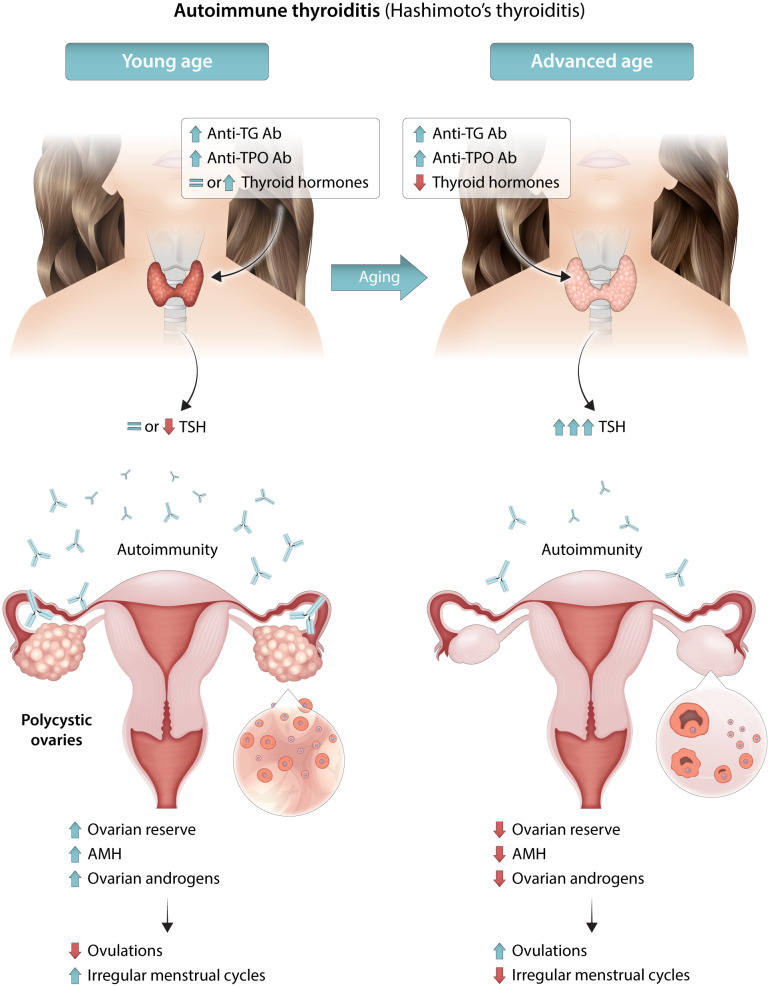
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration for the possible mechanisms underlying the relationship between AIT, ovarian reserve, PCOS severity and phenotype. During the initial phases, the autoimmune thyroiditis may cause an autoimmune inflammatory process also involving the ovaries and may predispose young women to PCOS or more severe PCOS phenotypes. At later phases, with an increase in age, auto-antibodies may damage ovarian tissue, as well as the thyroid gland. The reduced ovarian reserve may induce milder PCOS phenotypes. AIT, autoimmune thyroid disease; AMH, anti-Mullerian hormone; anti-TG Ab antithyroglobulin antibodies; anti-TPO Ab, anti-thyroid peroxidase antibody; PCOS, polycystic ovary syndrome.