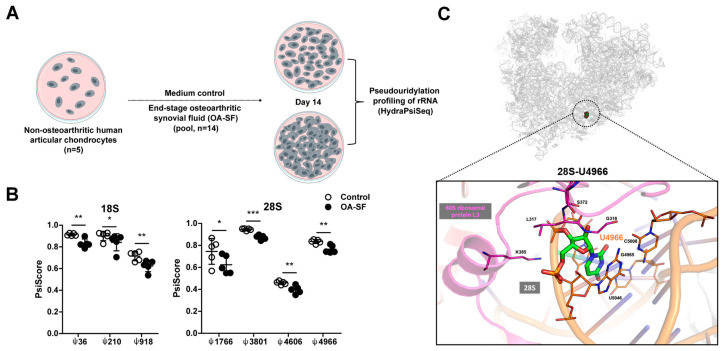
Figure 1.
The chronic disease microenvironment induces site-specific changes in the pseudouridylation levels of ribosomal RNAs in primary human chondrocytes. (A) A schematic of the experimental design. Non-OA human articular chondrocytes of 5 individual donors were exposed to a chronic disease microenvironment represented by the synovial fluid of end-stage OA patients (OA-SF, pool of 14 donors, 20% (v/v)) for 14 days. The culture medium was refreshed every other day. After 14 days of culture, total RNA was isolated and used for the pseudouridylation profiling of rRNAs by HydraPsiSeq. (B) Differentially pseudouridylated (ψ) rRNA nucleotides (n = 5). Statistical significance was assessed by paired t-test with the assumption of a normal distribution of the data. Full ψ rRNA profiles are shown in Figure S1 and PsiScore values are listed in Table S1. (C) Location of 28S-U4966 within domain VI of the large ribosomal subunit of the human ribosome. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.