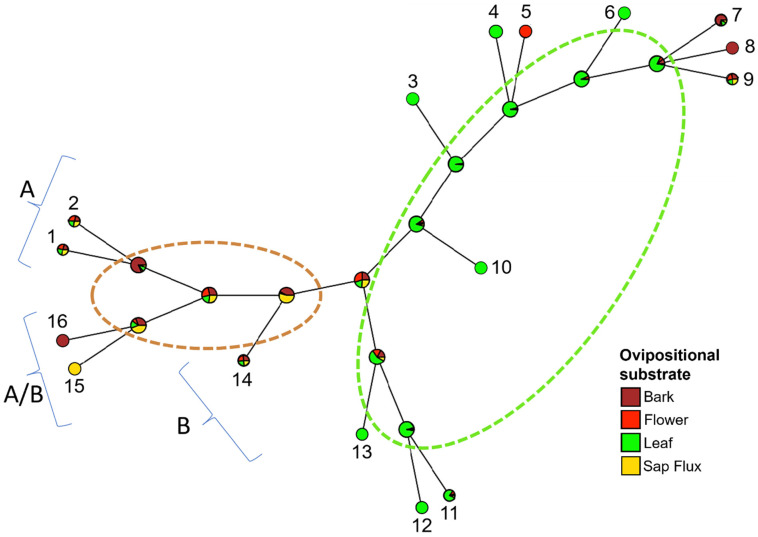
Figure 2.
Stochastic character mapping of the Hawaiian Drosophilidae (Drosophila and Scaptomyza) host species’ ancestral trait ‘ovipositional substrate’ (categories: bark, flower, leaf, and sap flux) mapped to an unrooted Wolbachia phylogeny. External nodes depict host trait assignments: solid = known, equal proportions = unknown. Interior nodes represent posterior probabilities that the host’s character trait is ancestral and congruent with the phylogenetic signal of the strain of their Wolbachia endosymbiont. Key to Wolbachia found in host individual listed in Supplementary S1 (sample number, species name): (1) 244 w D. nigrocirrus, (2) 16_1w D. “large spots” (double-infected strain A), (3) 185w D. ancyla, (4) 221w D. seclusa, (5) 20w S. caliginosa, (6) 216w D. nr. redunca, (7) 175w D. prostopalpis, (8) 123w D. prolaticilia, (9) 16_2w D. “large spots” (double-infected strain B), (10) 5w D. nr. basimacula #5, (11) 187w D. atroscutellata, (12) 145 w D. quasiexpansa, (13) 41w D. nr. basimacula #2, (14) 155 w D. micromyia, (15) 266w D. hawaiiensis, and (16) 247w D. engyochracea. Two strains belong to supergroup A, two were intermediate A/B, and all other strains belong to supergroup B.