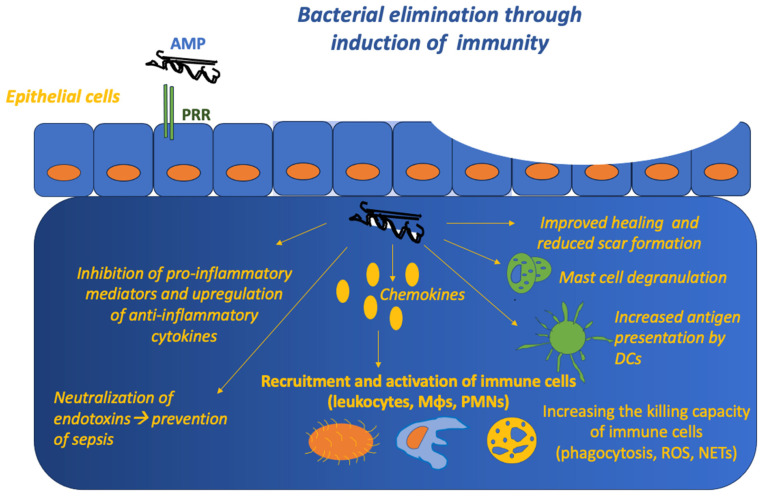
Figure 2.
Graphical representation showing the immunomodulatory function of AMPs. Apart from the direct killing mechanisms of AMPs, they can kill pathogens through the induction of innate and adaptive immunity. AMPs can induce cells involved in innate immunity, such as macrophages (Mφs), polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs), and mast cells. AMP: antimicrobial peptide; DCs: dendritic cells; Mφs: macrophages; PRR: pathogen recognition receptor; PMN: polymorphonuclear cell; ROS: reactive oxygen species; NETs: neutrophil extracellular traps.