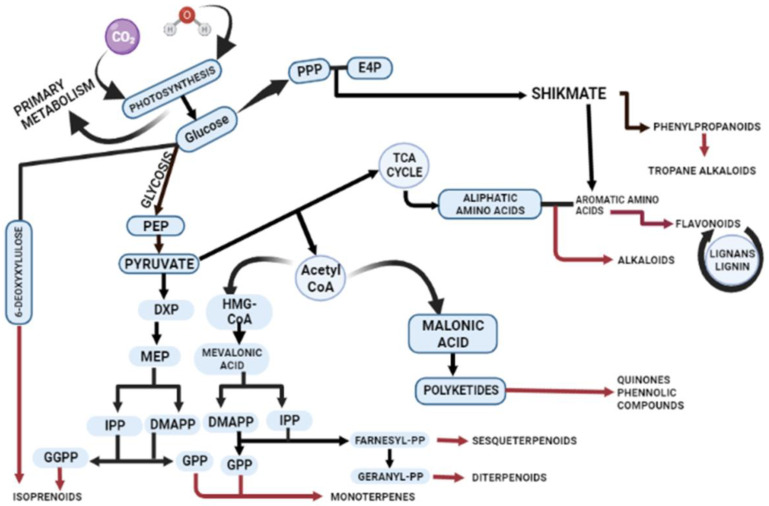
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of biosynthetic pathways for secondary metabolite production. The figure demonstrates the intricate biosynthesis of secondary metabolites and their interconnections with primary metabolism within plants. Plant cells employ diverse mechanisms through major pathways including mevalonic acid (MVA) and the 2-C-methylerythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) and shikmate pathway to synthesize terpenes, phenols, flavonoids, and alkaloids. Abbreviations: phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP); 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate (DXP); 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate (HMBPP); isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP); dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP); geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP); 2-C-methyl-l-erythritol 4-phosphate (MEP); 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate (DXP); acetyl coenzyme A (Acetyl-CoA); β-hydroxy β-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA); geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGPP); erythrose 4-phosphate (E4P); and pentose phosphate pathway (PPP).