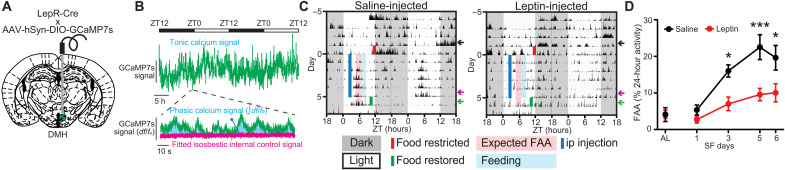
Fig. 3. FAA during fiber photometry recordings is dampened by leptin.
(A) Schematic diagram illustrating unilateral injection of AAV-hSyn-DIO-GCaMP7s and fiber optic cannula implantation to the DMH of LepRCre mice. (B) Example data trace illustrating two readouts of long-term fiber photometry calcium imaging. Tonic calcium signal represents the total fluorophore brightness. Phasic calcium signal represents the intracellular calcium activity over baseline activity in each recording session. See also fig. S5 for the second method of calculating these two readouts. (C) Representative locomotor actogram of single animals treated with saline (left) or leptin (right) during DMHLepR neuron GCaMP7s fiber photometry recording. Mice are housed in 12:12-hour LD cycle, fasted at lights off on day 5 (solid red line), injected with saline or leptin at 2.5 hours after lights on (ZT2.5; solid blue line), and fed at ZT6 (2 g on days 1 and 2 and 2.5 g on remaining days). Red-shaded area is the FAA time window 2 hours before meal time (ZT4 to ZT6), and blue-shaded area is the first 2 hours after food delivery (ZT6 to ZT8). Food is restored at ZT10 on day 6 of SF. Color-coded arrows indicate 3 days that are selected for quantification in Fig. 4. ip, intraperitoneal. (D) Quantification of FAA during long-term DMHLepR neuron GCaMP7s recording. FAA is defined as the locomotor activity in the 2-hour window before food delivery as a percentage of 24-hour activity. AL indicates ad libitum condition 2 days before initiation of drug administration. Mixed-effects (REML) analysis with Bonferroni post hoc comparison; n = 5 to 8 per group; Ftreatment(1,52) = 25.44, P < 0.001. Data are represented as means ± SEM. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001.