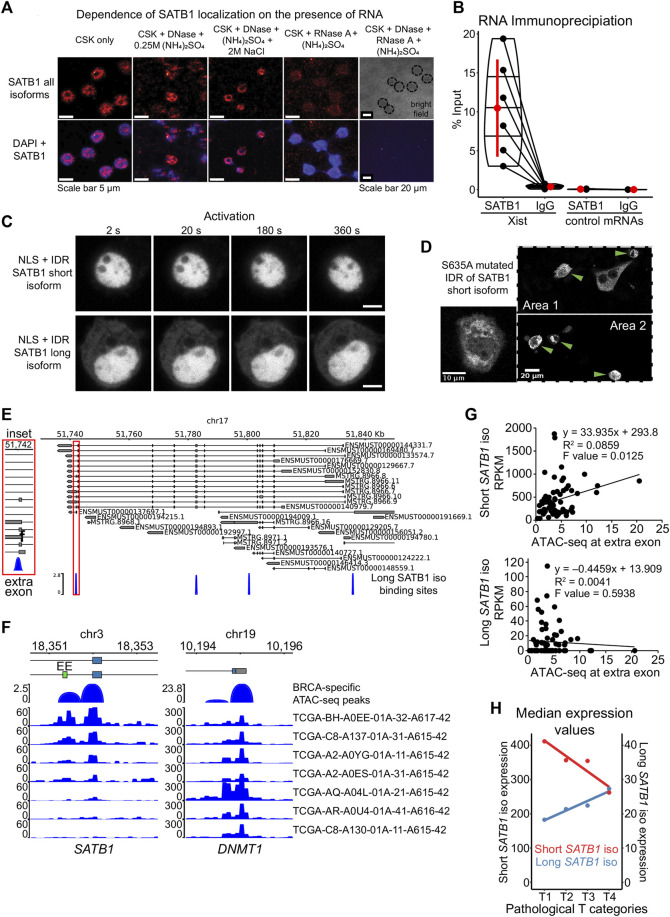
FIGURE 6.
Modes of regulation of SATB1 phase transitions. (A) Nuclear matrix extraction coupled to immunofluorescence analysis revealed that a fraction of SATB1 protein (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, sc-5990) remained in the cell nucleus even after DNase I treatment and high-salt extraction. However, RNase A treatment almost completely depleted SATB1 from the nucleus, indicating a high level of association between SATB1 and nuclear RNA. Representative of two biological replicates. (B) SATB1 co-immunoprecipitation confirmed the association of SATB1 with lncRNA Xist. Black dots represent individual % input measurements for Xist RIP (3 biological replicates, 4 Xist regions targeted) and control RIP experiments (3 biological replicates; 3 control RNAs: Tbp, Smc1a, Dxz4). The horizontal lines inside violin plots represent the 25th, 50th and 75th percentiles. Red circle represents the mean ± s.d. Mean fold enrichment for Xist RIP is 36 ± 20 s.d. (C) Forced nuclear localization of CRY2-mCherry constructs harboring the short or the long SATB1 isoform IDR and the SV40 NLS displayed no protein association in response to 488 nm laser activation. Scale bar 5 μm. (D) The S635A mutation, preventing phosphorylation of the short SATB1 isoform highly increased the aggregation propensity of the corresponding CRY2-mCherry-IDR construct. Green arrows indicate cells with the SATB1 aggregates. (E) Murine Satb1 transcripts reconstructed based on deeply-sequenced stranded-total-RNA-seq data. Both long and short Satb1 isoforms were produced from multiple promoters. The long SATB1 isoform binding sites were retrieved from GSE173446 (Zelenka et al., 2022). (F) Human TCGA breast cancer (BRCA) patient-specific ATAC-seq peaks (Corces et al., 2018) span the extra exon (EE; labeled in green) of the long SATB1 isoform. Note the differential chromatin accessibility in seven selected patients, emphasizing the heterogeneity of SATB1 chromatin accessibility in cancer. Chromatin accessibility at the promoter of housekeeping gene DNMT1 is shown as a control. (G) Increased ATAC-seq signal in human breast cancer patients is positively correlated with the expression of the short SATB1 isoform and negatively correlated with the long isoform expression. (H) In human breast cancer patients, high pathological T categories (indicating bigger extent of the primary tumor, presumably indicating worse prognosis; labeling based on the TNM cancer staging system) were associated with higher expression of the long SATB1 isoform. In contrast, the expression of the short SATB1 isoform was negatively correlated with the pathological T categories. Median RNA expression values for both isoforms based on all transcripts with non-zero expression values are displayed. Red circles represent the median values.