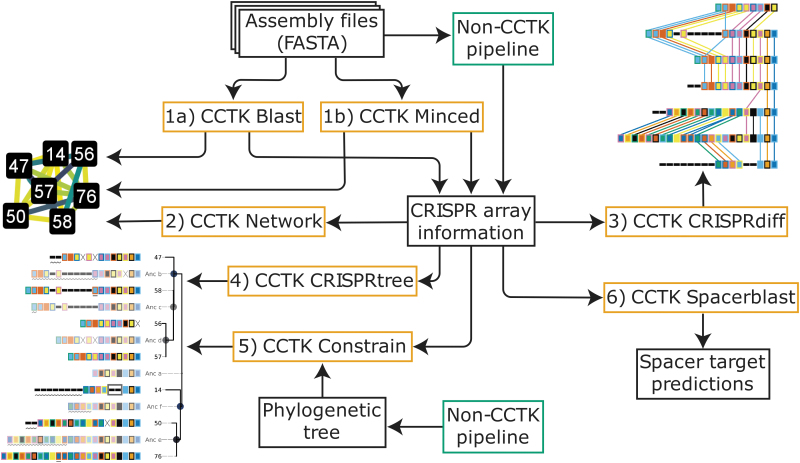
FIG. 1.
Flow of data through CCTK tools. Beginning with genome assemblies in FASTA format, CCTK tools can be used to identify and analyze CRISPR arrays. The six CCTK tools are as follows: (1a) Blast, (1b) Minced, (2) Network, (3) CRISPRdiff, (4) CRISPRtree, (5) Constrain, and (6) Spacerblast. The functions of each CCTK tool are described as follows: (1) CRISPR arrays can be identified in assemblies using either MinCED or BLASTn followed by processing steps that produce aggregated CRISPR information for all input assemblies. These CRISPR information files are used by downstream CCTK tools. Alternatively, non-CCTK tools can be used to identify arrays, and their output easily adapted to the simple file formats used by CCTK. (2) The relationships between CRISPR arrays can be represented as a network in which each array is represented as a node. Homologous arrays (i.e., arrays containing identical spacers) are connected by an edge, the weight of which corresponds to the Jaccard similarity between the two arrays. (3) Groups of homologous arrays can be visualized using CRISPRdiff to identify the differences and similarities between arrays. (4) CRISPRtree can infer a phylogenetic tree representing the relationships between homologous arrays and can hypothesize events that occurred during their history. (5) Constrain can visually represent how CRISPR arrays may have evolved given a fixed tree topology to allow the reconciliation of CRISPR relationships with other phylogenetic data. (6) Spacerblast predicts protospacer targets of CRISPR spacers and determines the presence of a PAM. CCTK, CRISPR comparison toolkit; PAM, protospacer adjacent motif.