Figure 2. Interactions Between Motoric Cognitive Risk Syndrome (MCR) Assessment and Objective Cognitive Impairment (OCI) on the Associations With Car Collisions and Near-Miss Traffic Incidents .
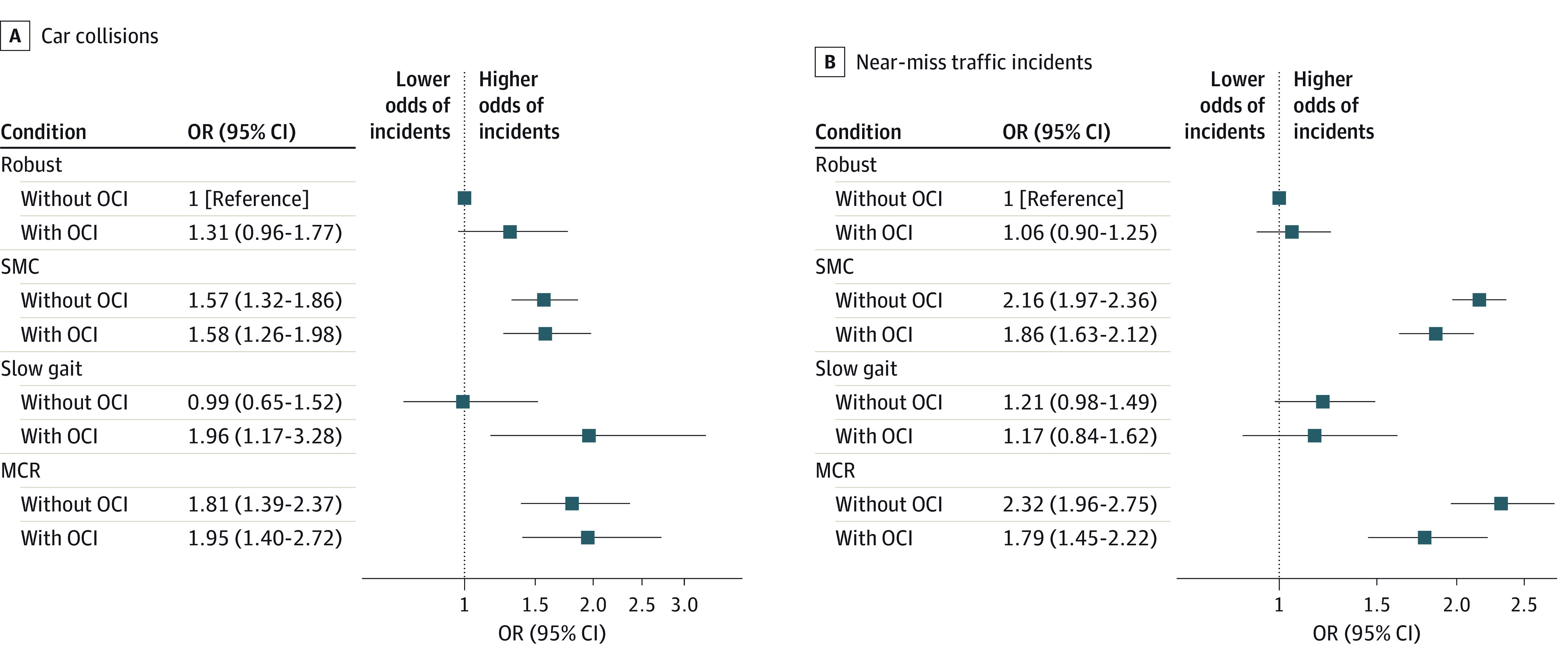
Odds ratios (ORs) were adjusted for age, sex, educational year, eye diseases, hearing difficulty, medication use, sleep duration, excessive daytime sleepiness, and driving time. MCR indicates motoric cognitive risk syndrome; OCI, objective cognitive impairment; SMC, subjective memory concerns.
