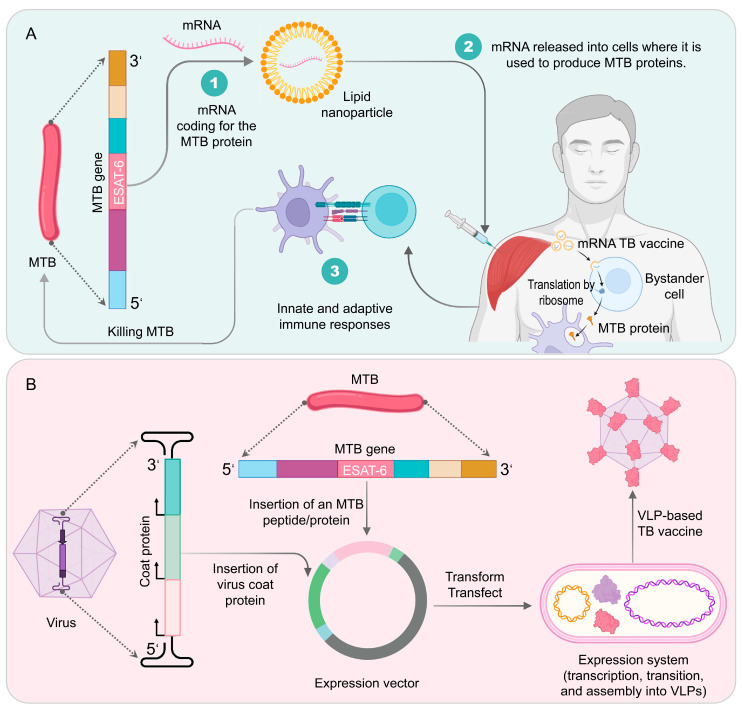
Figure 5.
Illustrates the generation of mRNA TB vaccines and VLP-based TB vaccines. In (A), the DNA encoding the target protein of MTB is obtained and transcribed into mRNA. The mRNA is then loaded with lipid nanoparticles and other carriers to create a TB mRNA vaccine for intramuscular immunization. When these mRNA vaccines are injected into the human body, ribosomes in bystander cells assist in translating the target protein. Bystander cells engulf the produced protein, activating both innate and adaptive immune responses to eliminate MTB. In (B), a coat protein from a virus is cloned into an expression vector. The expression vector is then modified to include the MTB protein, such as ESAT-6 or CFP-10. The resulting expression vector contains both the coat protein and the MTB protein. It is transformed or transfected into an expression system to produce the proteins. Finally, the MTB protein assembles into VLPs, resulting in a VLP-based TB vaccine.