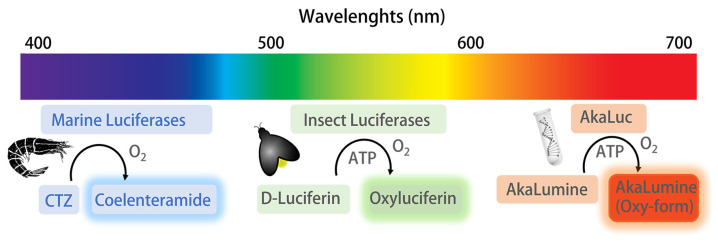
Figure 2.
BL luciferase–luciferin pair systems obtained from marine and terrestrial organisms, and from engineered proteins. The BL reaction from marine organisms involves the oxidation of coelenterazine (CTZ) substrate by luciferase; CTZ is converted to the coelenteramide form, emitting photons in the blue light region (454–493 nm). BL reactions from insects involve the oxidation of D-luciferin in two distinct steps, in the presence of ATP, to obtain the oxyluciferin form, emitting photons in the green-red region of the visible spectrum. The AkaLuc system involves the use of an engineered firefly luciferase AkaLuc optimized to catalyze the oxidation of unnatural luciferin AkaLumine substrate to obtain the AkaLumine oxy-form, emitting photons in the near-infrared region.