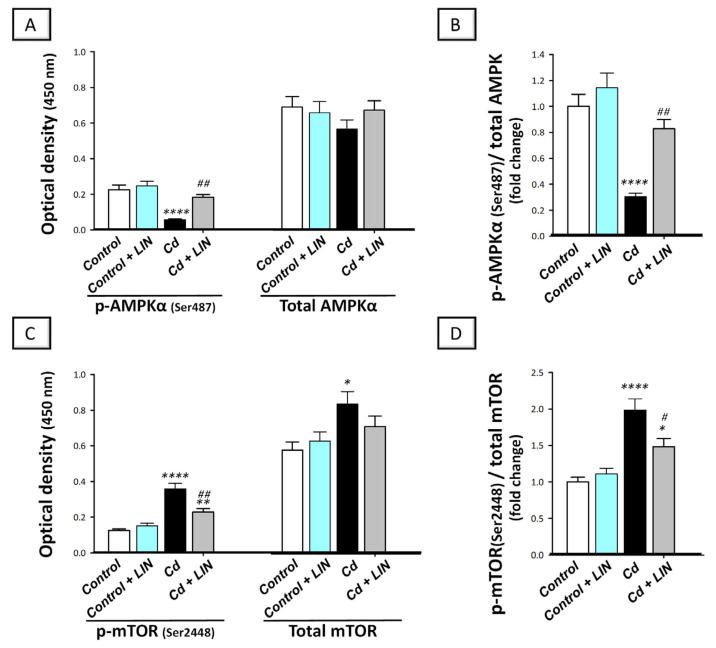
Figure 8.
Linagliptin stimulates hippocampal AMPK/mTOR pathway in cadmium-intoxicated rats. Herein, stimulation of AMPK/mTOR pathway by linagliptin in cadmium-intoxicated animals was reflected by the elevation in p-AMPK/AMPK ratio (B), and reduction in p-mTOR/mTOR ratio (D). Of note, the individual O.D. of p-AMPK(Ser487) and total AMPK are shown in (A), whereas the individual O.D. of p-mTOR(Ser2448) and total mTOR are shown in (C). For each experimental group, the mean optical density of either p-AMPK or p-mTOR was divided by the corresponding mean optical density of the total AMPK or total mTOR, respectively. This was followed by setting the mean control value to 1. N = 6 in each group (mean ± standard error of the mean). A p-value of less than 0.05 was significant. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, or **** p < 0.0001, compared to control; # p < 0.05, or ## p < 0.01, compared to cadmium (Tukey’s test for multi-comparisons and one-way ANOVA). AMPK, 5′adenosine-monophosphate-activated protein kinase/ mammalian target of rapamycin; Cd, cadmium chloride; LIN, linagliptin; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin.