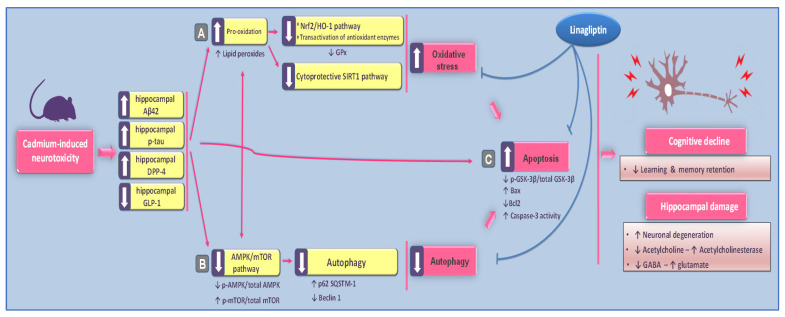
Figure 9.
A summary of the proposed molecular pathways for linagliptin’s neuroprotection against the cognitive impairment induced by cadmium in rats. Based on the current findings, linagliptin ameliorated cadmium-induced retention/recognition memory disruption and neuronal degeneration by augmenting the hippocampal GLP-1 levels. The dampened cadmium-induced neurotoxicity was manifested by lowered hippocampal Aβ42 and p-tau noxious signals alongside augmenting acetylcholine/GABA and lowering neurotoxic glutamate. At the molecular level, these favorable effects were brought by (A) combating hippocampal oxidative insult and stimulation of SIRT1/Nrf2/HO-1 cytoprotective pathway; (B) stimulation of the pro-autophagy response and activation of AMPK/mTOR cascade; (C) reversal of hippocampal apoptotic machinery and inactivation of the pro-apoptotic kinase GSK-3β. Arrows: an arrow with a solid line denotes activation; an arrow with a blunt line indicates inhibition.