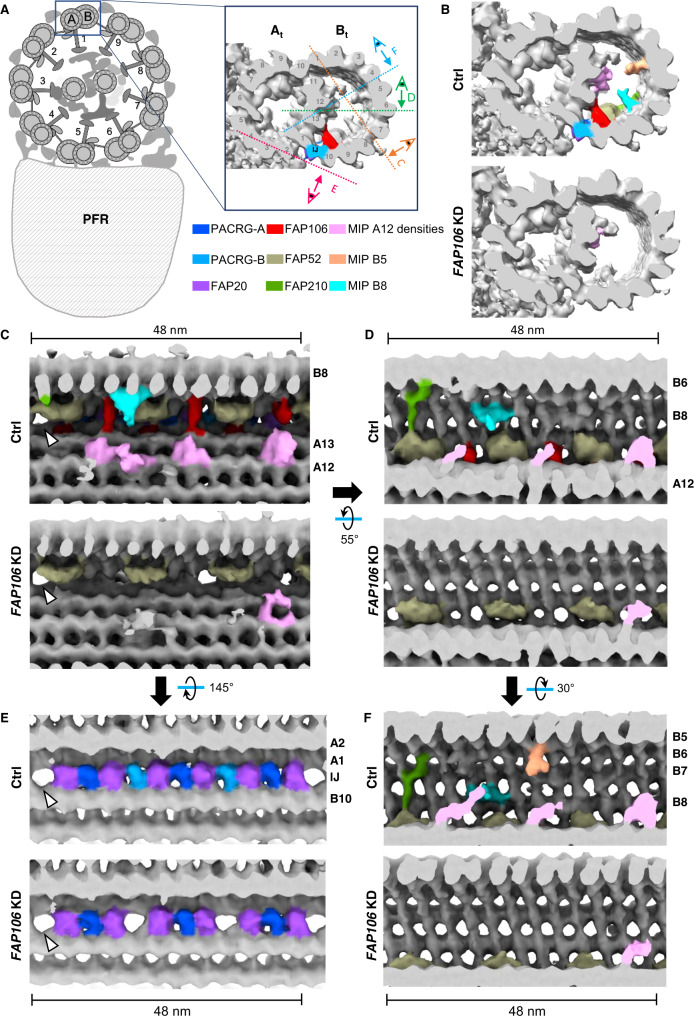
Fig. 2. FAP106 is required for assembly of conserved and lineage-specific MIP structures.
Demembranated flagella were purified from 29-13 (Ctrl) and FAP106 knockdown (FAP106 KD) parasites grown in tetracycline to induce knockdown. Structure of the 48-nm repeat of the DMT was obtained by cryoET, with sub-tomographic averaging. Densities are shown as surfaces and colored according to the legend. Conserved MIPs are colored based on similarity to published structures13,15,21 (Supplementary Fig. 3). Lineage-specific densities (MIP A12, MIP B5, MIP B8) not present in Chlamydomonas or bovine structures are colored to highlight densities that are substantially reduced in FAP106 KD. A Schematic illustrating a cross-section of the “9 + 2” axoneme and paraflagellar rod (PFR) viewed from flagellum tip to base. Adapted from75. Enlarged panel shows a single DMT, with A- and B-tubules indicated (At, Bt) and protofilaments numbered. FAP106 (red) and the inner junction filament (IJ) comprised of alternating PACRG (blue) and FAP20 (purple) are colored for reference. Viewing angles shown in (C–E) are indicated. B Cross-sectional view of the DMT. Colored densities indicate structures reduced or missing in FAP106 KD compared to Ctrl. C, D Longitudinal views of the DMT. Viewing angles are indicated in (A), inset. The 48-nm repeat is indicated. Note that T. brucei has a structure similar to FAP210 (green) despite not having a clear FAP210 homolog (Table 1). White arrowheads indicate the position of the single hole found within each 48-nm repeat in Ctrl DMTs. E Longitudinal views of the DMT, showing the IJ filament. Viewing angles are indicated in (A), inset. The 48-nm repeat is indicated. White arrowheads indicate the position of the single hole found within each 48-nm repeat in Ctrl DMTs. FAP20 and PACRG subunits are colored according to the legend. PACRG-A and PACRG-B are colored to be consistent with TMT proteomics data showing that only PACRG-B is lost in FAP106 KD (Fig. 3A and Supplementary Data 1), which suggests the extra holes in the FAP106 KD structure correspond to the position of PACRG-B in control axonemes. F Longitudinal view showing reduction of MIP B5 in FAP106 KD.