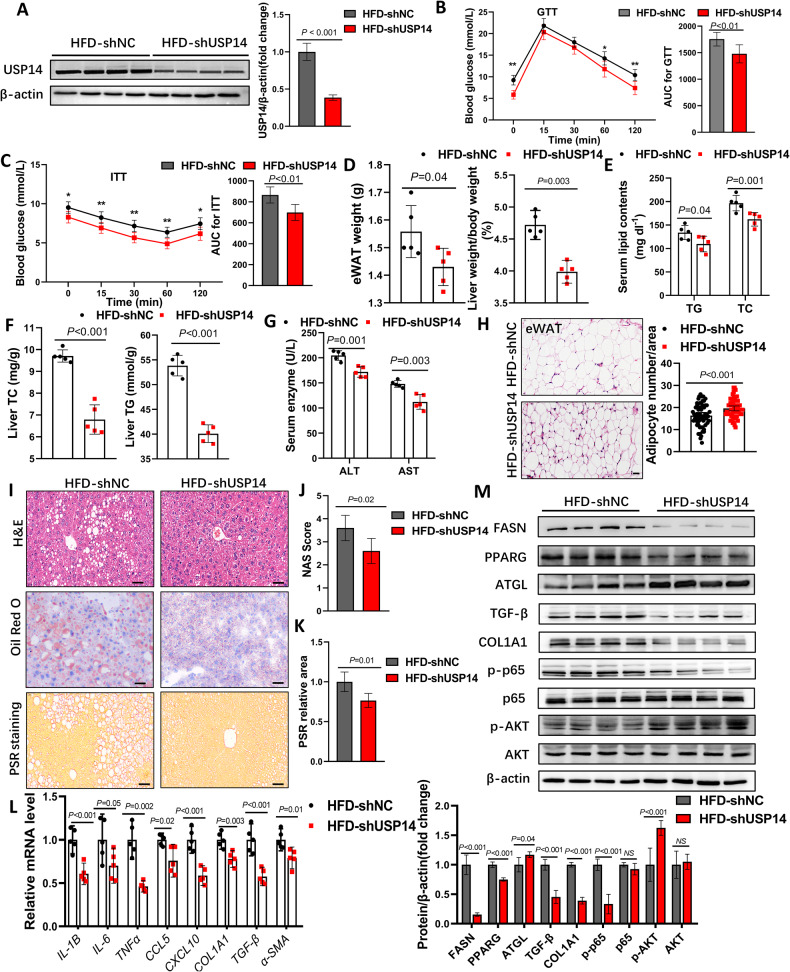
Fig. 3. Knockdown of hepatic USP14 alleviates the HFD-induced NAFLD progression.
A USP14 protein levels in livers of shNC or shUSP14 adenovirus-treated mice. B, C GTT and ITT analysis of mice 5 weeks after shNC or shUSP14 adenovirus injection (n = 12). AUC, area under the curve. D Effect of shNC or shUSP14 adenovirus injection on eWAT weight and LW/BW ratios in mice (n = 5). E–G Effect of shNC or shUSP14 adenovirus injection on serum or liver TG and TC levels and serum AST and ALT levels in mice (n = 5). H H&E staining and adipocyte counts of eWAT (n = 5). I H&E staining, oil red O staining, and PSR staining from the livers of mice in each group (n = 5). Scale bar, 50 μm. J, K NAS score and relative PSR area from each group of mice. L Expression of inflammatory and fibrotic genes in the liver of each group of mice (n = 5). M Expression of lipid metabolism-related proteins, inflammation-related proteins, fibrosis-related proteins, and insulin sensitivity-related proteins in the liver of mice in each group. * P < 0.05 for the HFD-shNC compared to the HFD-shUSP14 group; ** P < 0.01 for the HFD-shNC compared to the HFD- shUSP14 group. NS not significant.