Figure 3. In vivo imaging with ultrasound-based technologies.
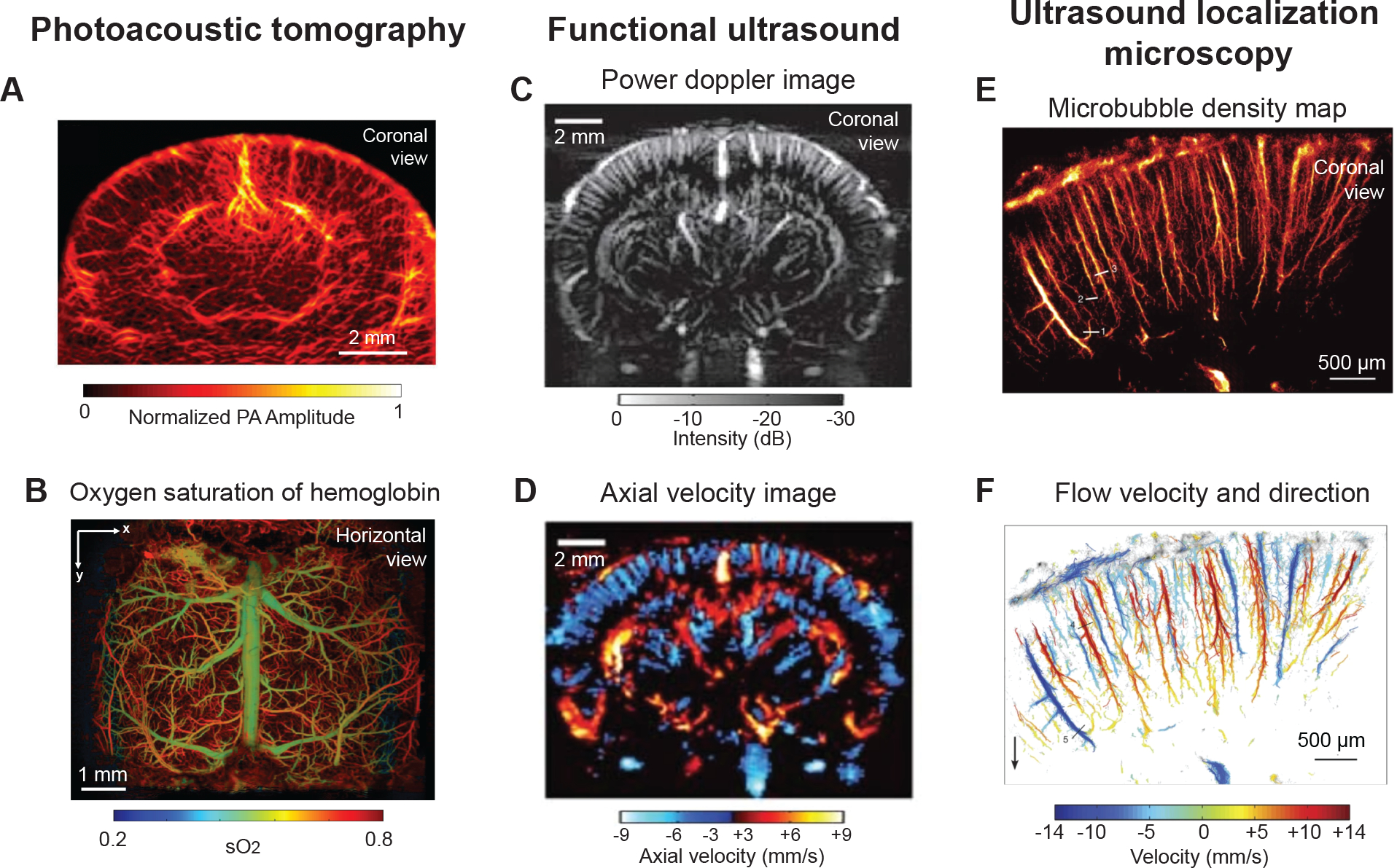
(A) Photoacoustic computed tomography image providing coronal view of mouse brain through an intact skull. Used with permission of John Wiley & Sons, from High-resolution deep functional imaging of the whole mouse brain by photoacoustic computed tomography in vivo, Zhang P, 11, 2018; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.97 (B) Horizontal view showing oxygen saturation of blood in vasculature from dorsal surface of mouse brain, collected by ultra-fast wide-field photoacoustic microscopy. Images were collected after skull removal and implantation of a whole cortex window. Adapted from Zhu et al.99 (C,D) Entire depth of rat brain imaged through a bihemispheric transcranial window using fUS. Panel C shows power Doppler image and panel D shows axial blood velocity image revealing domains perfused by penetrating vessels. Adapted from Macé et al.104 with permission. Copyright ©2011, Springer Nature. (E,F) Magnified view of cortical microvessels imaged by ultrasound localization microscopy. Panel E shows microbubble density map and panel F shows flow velocity and flow direction map revealing individual cortical penetrating arterioles and ascending venules. Adapted from Errico et al.108 with permission. Copyright ©2015, Springer Nature.
